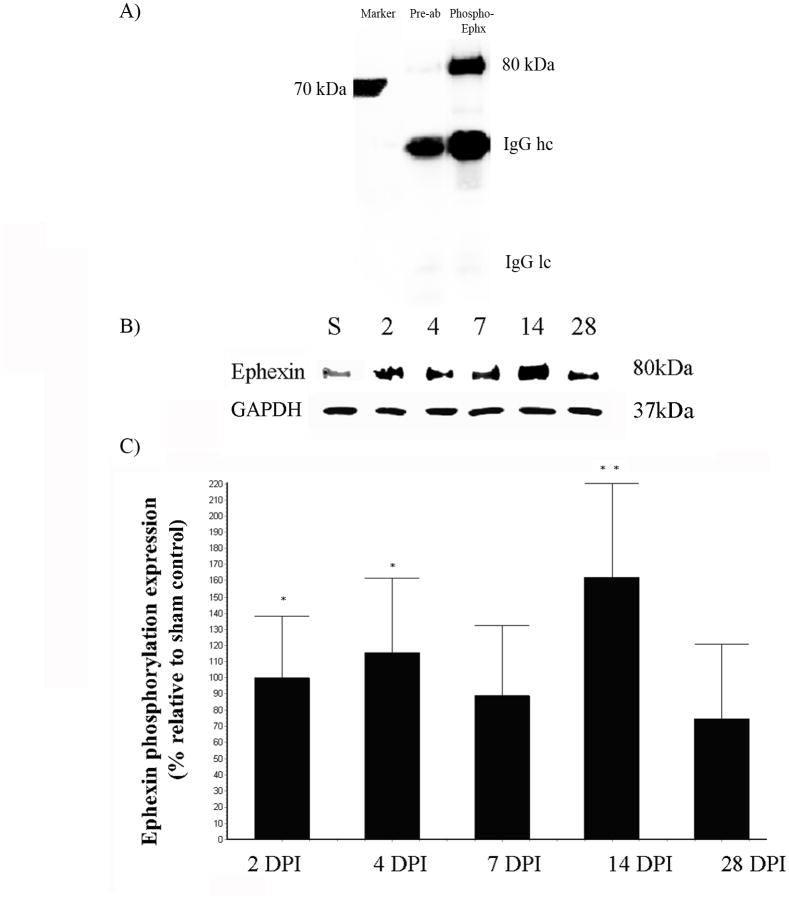
Figure 4.
Trauma to the spinal cord induces ephexin phosphorylation. Anti-phospho Ephexin immunoprecipitated specifically the activated protein (80 kDa) from spinal cord extracts and preabsorption assay demonstrated the specificity of the antibody used (A). Immunoprecipitation showed the activation of ephexin at the lesion epicenter at 2, 4, 7, 14 and 28 DPI. Extracts for each time point were analyzed by Western blot against GAPDH to demonstrated equal amount of proteins for the immunoprecipitation assay (B). Densitometry analysis of phospho-ephexin showed a significant increase at 2 (*p<0.05), 4 (*p<0.05) and 14 DPI (**p<0.01) (C). ANOVA followed by Dunnett test was used to determine the significant differences (F= 4.285 df(5,27), p<0.0053). Error bars demonstrate the standard error of the mean (SEM), 2DPI and 4 DPI (n=5); 7 DPI and 14 DPI (n=3) and 28 DPI (n=4).