Figure 3.
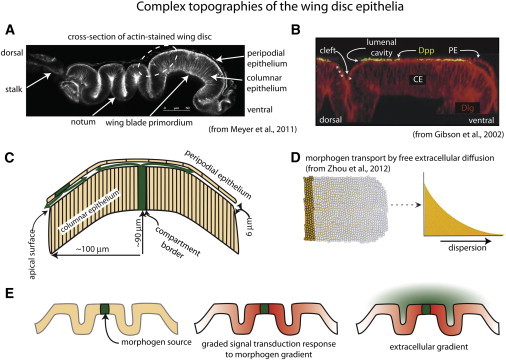
Complex topographies of the wing disc epithelia. (A) Cross section showing folds of the disc layers (from Meyer et al. (17)). The disc was stained with phalloidin and mounted on its side. (B) The fluorescent micrograph is a slightly flattened cross section of the region indicated by dashed white oval in A from a disc stained with α-Dpp antibody for external Dpp and α-Dlg (from Gibson et al. (4)). Note the presence of Dpp in the lumenal cavity, and Dpp along the surface of the CE in the lumenal cleft (stars), but the absence of Dpp in the space that forms at the lumenal cleft (arrow) between the CE and the PE. (C) The drawing depicts a cross section of the wing blade primordium, showing the spatial juxtaposition of the columnar and peripodial layers and domed shape. Green arrows represent the presumed paths of Dpp in the lumenal cavity. (D) Pictorial and graphical representations of morphogen that disperses by free extracellular diffusion (from Zhou et al. (1)). (E) Drawings depict folds of an epithelium (left), the presumed response of cells in the epithelium (red) to a continuous concentration gradient of morphogen (green, middle), and the lack of correlation of the response of the epithelium to the theoretical distribution of morphogen if it disperses by free diffusion in the extracellular space at the upper surface of the epithelium (right).
