Figure 2.
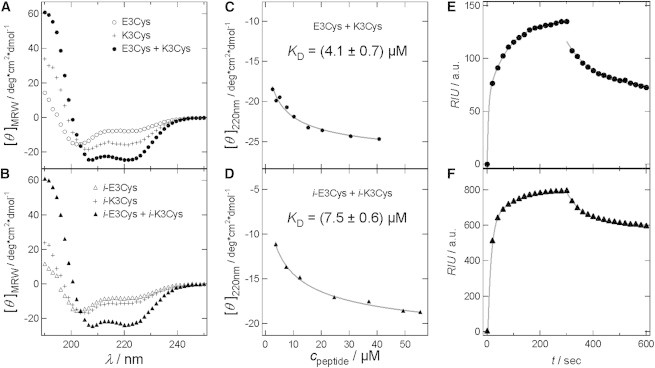
(A–D) CD spectra and analysis to determine the dissociation constant of coiled-coil dimers. (A) E3Cys (open circles), K3Cys (crosses), and a mixture of both (solid circles) in PB 6.8. (B) i-E3Cys (open triangles), i-K3Cys (crosses), and the corresponding mixture (solid triangles). (C and D) Concentration dependence of [θ]MRW at 220 nm of heterodimeric coiled-coil to determine KD for E3Cys and K3Cys (C), and for i-E3Cys and i-K3Cys (D; fits of Eq. 1 are shown as gray lines (22)). (E and F) Association (t = 0–300 s) and dissociation (t = 300–600 s) of E-peptides coupled to immobilized K-peptides on a hydrogel monitored by SPR spectroscopy. Association of peptides was fitted by a double exponential function to obtain kon, whereas dissociation of the peptide assembly was fitted by a monoexponential function (koff; see Supporting Material; gray lines). (E) E3Cys was added to immobilized K3Cys at a concentration of 15 μM (solid circles). KD = (0.5 ± 0.3) μM. (F) i-E3Cys was added to immobilized i-K3Cys at a concentration of 15 μM (solid triangles). KD = (2.3 ± 1.8) μM.
