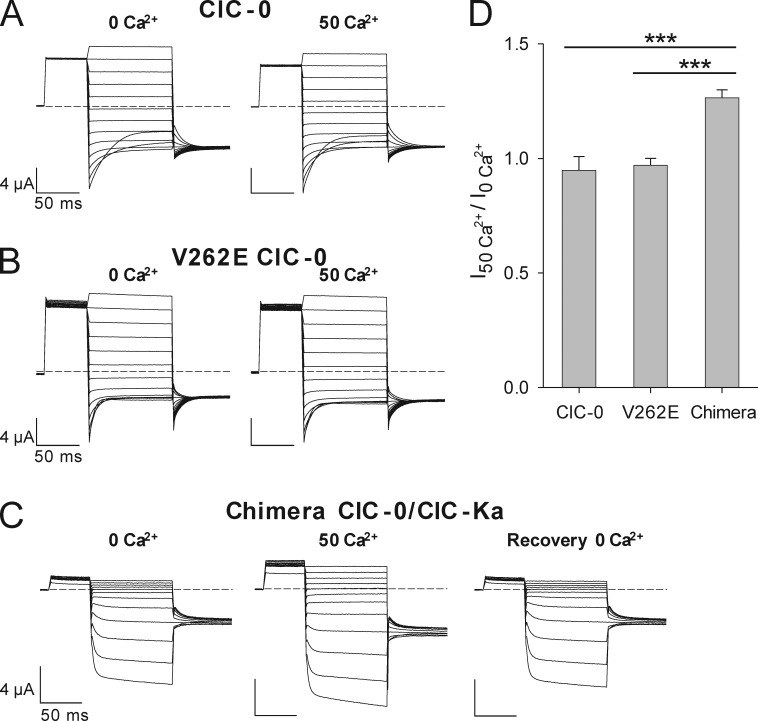
Figure 4.
Conferring Ca2+ dependence onto ClC-0. Typical currents of ClC-0 constructs evoked by the fast gate protocol (see Materials and methods) at nominal 0 and at 50 mM Ca2+. (A–C) Currents of WT ClC-0 (A) and its mutant V262E (B) are not affected by increasing external Ca2+, whereas currents of the ClC-0/ClC-Ka chimera (C) are potentiated. (D) Effect of 50 mM Ca2+ on the current magnitude of WT ClC-0 (n = 4), V262E ClC-0 (n = 5), and chimera ClC-0/ClC-Ka (n = 8). Currents acquired at −100 mV at 50 mM Ca2+ concentration were normalized to the values recorded at nominal 0 Ca2+. WT ClC-0 and mutant V262E currents were recorded after maximal activation of the slow gate by repetitive hyperpolarization. Potentiation of the chimera by Ca2+ is highly significant, as indicated by the asterisks (***, p-values of I50Ca2+/I0Ca2+ between chimera and WT ClC-0 or chimera and V262E are < 0.5 × 10−6, unpaired Student’s t test). Error bars indicate SD.