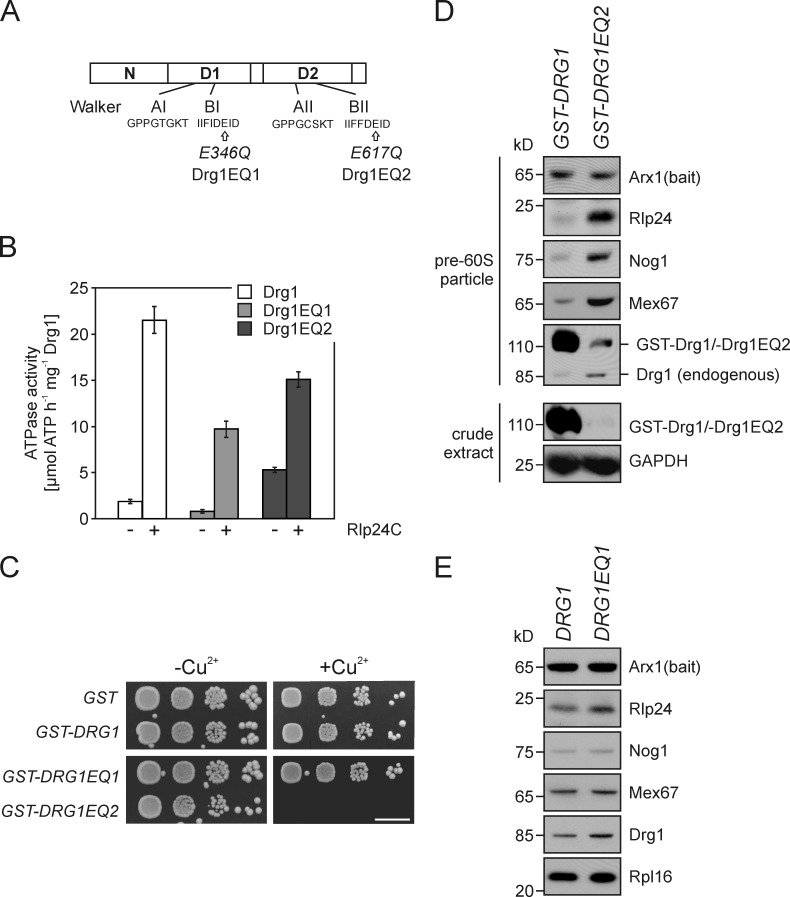
Figure 3.
Inactivation of ATP hydrolysis in the D2 domains of Drg1 blocks the release of shuttling proteins. (A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of Drg1. The positions of the respective E to Q amino acid exchanges in the Walker B motifs of the first (Drg1EQ1) and second (Drg1EQ2) AAA domain of the two mutants are indicated. (B) The ATPase activity of both AAA domains is stimulated by Rlp24. The ATPase activity of Drg1, Drg1EQ1, or Drg1EQ2 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 800 nM Rlp24C was determined. Error bars: SD of at least two biological replicates. (C) Overexpression of the Drg1EQ2 but not of the Drg1EQ1 protein results in a dominant-negative growth phenotype. Spot assay to monitor growth under uninduced (−Cu2+) or induced (+Cu2+) conditions. Serial dilutions of strains expressing GST fusions of Drg1, Drg1EQ1, and Drg1EQ2 under the control of the CUP1 promoter were spotted on SDC–ura plates containing 0.5 mM CuSO4. Growth was monitored after incubation at 30°C for 3 d. Bar, 10 mm. (D) Overexpression of the Drg1EQ2 protein causes accumulation of shuttling proteins and export factors on late pre-60S particles in a wild-type background. The Drg1EQ2 protein or wild-type Drg1 were expressed as GST fusions under the control of the Cu2+-inducible CUP1 promoter in an Arx1-TAP strain. Cells were grown to early log phase and the CUP1 promoter was induced with 0.5 mM CuSO4 for 3 h. Afterward, pre-60S particles were isolated by protein A affinity purification and TEV elution. Purified particles were analyzed for the presence of pre-60S factors by Western blotting. Note that despite the low expression level of Drg1EQ2 (see protein levels in the crude extract), binding of the mutant protein and an accumulation of shuttling proteins occurred. (E) The composition of late pre-60S particles does not change significantly when ATP hydrolysis is blocked in the D1 AAA domain. Pre-60S particles were affinity purified with Arx1-TAP as bait protein from the drg1Δ strain ectopically expressing Drg1 or Drg1EQ1 from centromeric plasmids under the control of their native promoters. The TEV eluates were analyzed for the presence of shuttling proteins by Western blotting.