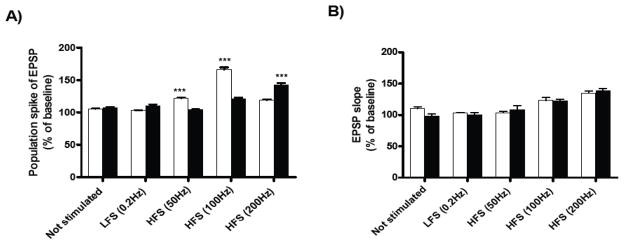
Figure 2.
Effects of HFS on short-term potentiation in hippocampal slices from 5-weeks-old TgCRND8 mice and their age-matched WT controls. Short-term- potentiation was measured in the pyramidal cell layer of the CA1 region following high-frequency stimulation (50Hz, 100Hz or 200Hz) of the Schaffer collaterals. Values of the amplitude of the population spike (A) and fEPSP slope (B) are expressed as percentages compared to their own baselines normalized to 100%. Each graph shows the mean ± S.E.M. of the first 15 min of recording after tetanus. The data were analyzed using a Two-way ANOVA in a within-subjects design, followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc tests for pair-wise comparisons. Significant difference was designated as ***p<0.001. The results show a significant increase in synaptic plasticity at 50Hz and 100Hz of slices from WT mice (white bar, n=4 slices per group) and for TgCRND8 mice at 200Hz (black bar, n=4 slices per group) in the amplitude of the population spike. There were no significant differences in the fEPSP slope between groups.