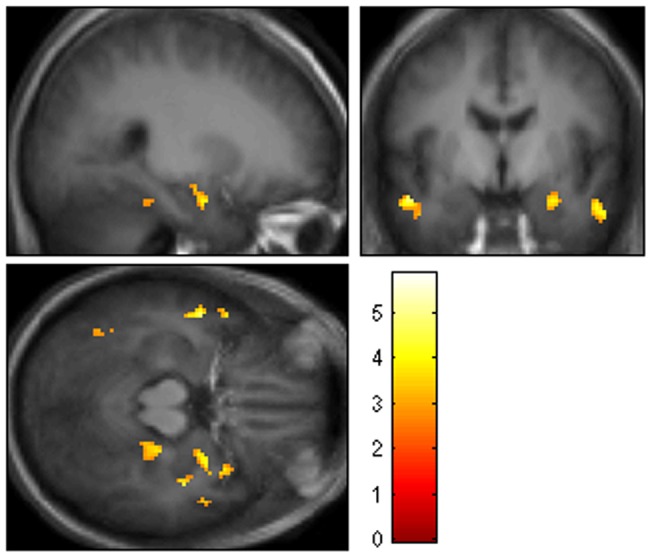
Figure 3. Brain regions showing significant positive correlation between the duration of nocturnal hypoxemia and effects of task load in DMN (ie, regions where increased duration of nocturnal hypoxemia correlates with less effective deactivation of DMN regions with increasing task load; MNI coordinates, corrected for multiple comparisons, p = 0.05, neurological presentation).