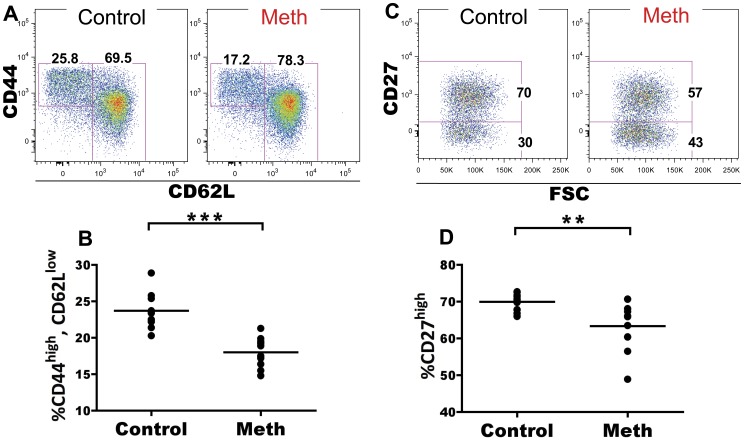
Figure 5. Meth reduces proportions of CD62Llow, CD44high splenic CD4 T cells and these cells exhibit lower CD27 expression.
Splenic CD4 T cells were examined after meth treatment to determine if meth alters surface phenotypes suggesting activation/antigen experience and effector status. A. Representative gating showing CD62L and CD44 on CD4 T cells. B. Meth causes a reduction in proportion of CD44high, CD62Llow CD4 T cells. C. CD27 expression by CD44high, CD62Llow CD4 T cells. D. CD44high, CD62Llow CD4 T cells from meth treated animals exhibit a lower proportion of cells expressing CD27 at a high level. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 calculated by Mann-Whitney U Test. Bars represent mean. Data are from 2 experiments of 5 animals per treatment group per experiment.