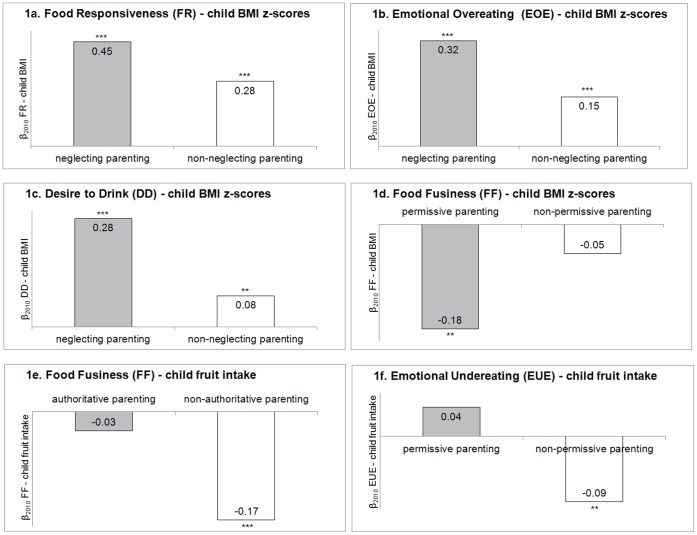
Figure 1. Significant moderating effects of parenting styles on the longitudinal associations between CEBQ subscales and child intake/child BMI z-scores in 2010.
Moderation testing was performed on significant longitudinal associations between CEBQ scales and (changes in) child intake/child weight (Table 2, column ‘β2010’ and column ‘β2010-2009’). pinteraction term Figure 1a = 0.023; pinteraction term Figure 1b = 0.082; pinteraction term Figure 1c = 0.018; pinteraction term Figure 1d = 0.068; pinteraction term Figure 1e = 0.020; pinteraction term Figure 1f = 0.038. * correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed); ** correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed); *** correlation is significant at the 0.001 level (2-tailed).