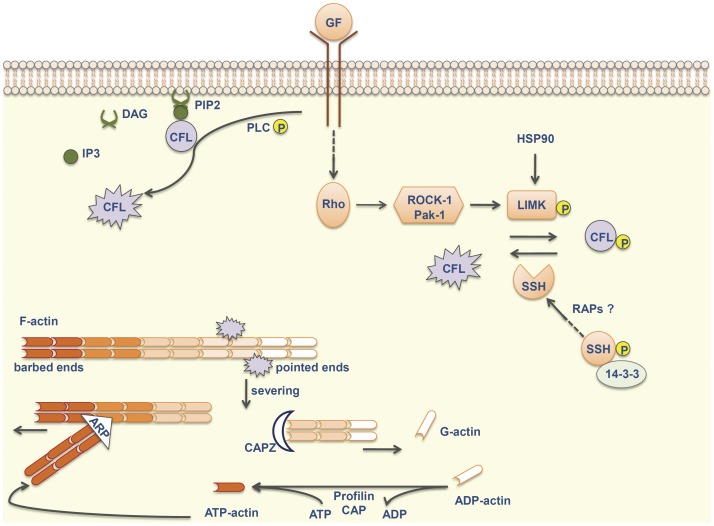
Figure 5. Cofilin pathway.
Microenvironmental stimuli signal through Rho-GTPases and their regulating kinases (ROCK1 and Pak-1), stimulating LIMK to phosphorylate and inactivate cofilin-1. Otherwise, SSH phosphatases dephosphorylate cofilin. Rap proteins may increase the enzymatic activity of SSHs, possibly by promoting their release from 14-3-3 proteins. Cofilin is sequestered by PIP2 and released after hydrolysis of PIP2 by phosphorylated PLC to IP3 and DAG. The active cofilin severs “old” actin filaments to generate free actin barbed ends. ATP-actin assembles into these barbed ends and ADP-actin subunits are, in turn, dissociated from the pointed end. Free actin monomers exchange ADP to ATP, frequently with the help of profilin and CAP proteins. ARP2/3 complex binds to F-actin and nucleates the growth of daughter filaments, generating a dendritic network at the leading edge of migratory cells. Other members of this pathway include Hsp90, which promotes stability of LIMK, and CAPZ, which interacts with barbed ends and inhibits filament assembly. ARP = actin-related protein 2/3 complex; CAP = adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1; CAPZ = F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-1; CFL = cofilin-1; F-actin = filamentous actin; DAG = diacylglycerol; G-actin = globular actin; GF = growth factor; HSP90 = heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha; IP3 = inositoltrisphosphate; LIMK = LIM kinases; Pak-1 = serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1; PIP2 = phosphatidylinositol-4-5-biphosphate; PLC = phospholipase C; RAP = Ras-related protein; ROCK-1 = Rho-associated protein kinase 1; SSH = slingshot phosphatase.