Figure 3.
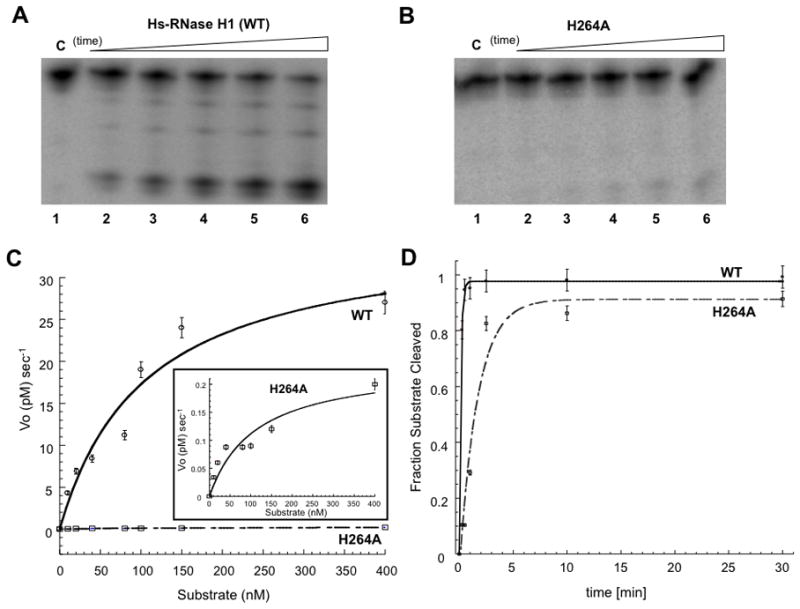
Defective catalytic activity of the H264A mutant. Panels A and B display phosphorimages of time course assays of hybrid substrate cleavage by Hs-RNase H1 and the H264A mutant, respectively, under steady-state (substrate excess) conditions. The assay used 150 nM RNA•DNA (preformed) hybrid and 10 nM enzyme. Reactions were initiated by adding Mg2+ (10 mM final concentration) followed by incubation at 30°C in a buffer containing 150 mM KCl, 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), and 10 mM DTT. Aliquots were combined with excess EDTA at specified times and analyzed by electrophoresis in a 15% denaturing polyacrylamide gel as described in Materials and Methods. In panel A, lanes 1–6 display 0, 1, 2.5, 5, 10, and 30 min time points, respectively, and in panel B, lanes 1–6 display 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 30, and 60 min time points, respectively. C. Michaelis-Menten steady-state analysis. The initial rate (Vo) was obtained as a function of substrate concentration. A best-fit curve to a Michaelis-Menten scheme is shown, with each point representing the average of two experiments. The inset has an expanded vertical axis, to better display the substrate concentration dependence of initial rate of cleavage by the H264A mutant. D. Single-turnover kinetic analysis. 5′-32P labeled RNA•DNA (preformed) hybrid (5 nM) was reacted at 30°C with Hs-RNase H1 or H264A mutant (50 nM) in buffer containing 150 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), and 10 mM DTT. Reactions were initiated by adding MgCl2, and aliquots quenched with excess EDTA at the specified times, followed by analysis by denaturing PAGE (see Materials and Methods). Lanes 1–6 display 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2.5, and 5 min reaction times for Hs-RNase H1, and lanes 7–12 represent the same time points for the H264A mutant. The graph displays the fraction of RNA cleaved as a function of time. Shown are the best-fit curves to a single exponential equation, using Kaleidagraph software. The exponential time constant is 0.6 ± 0.2 min for Hs-RNase H1, and 6.9 ± 0.4 min for the H264A mutant.
