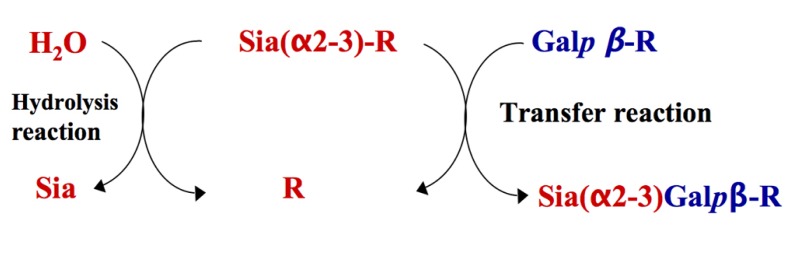
FIGURE 2.
Representation of transfer and hydrolysis activities of TcTS. TcTS preferentially catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid residues from Siaα2–3Galβ1-R containing donors and attaches them in α2–3 linkage to terminal β-Galp containing acceptors (transfer reaction). In the absence of a carbohydrate acceptor, TcTS irreversibly transfers sialic acid to a water molecule, thus functioning as a sialidase (hydrolysis reaction).