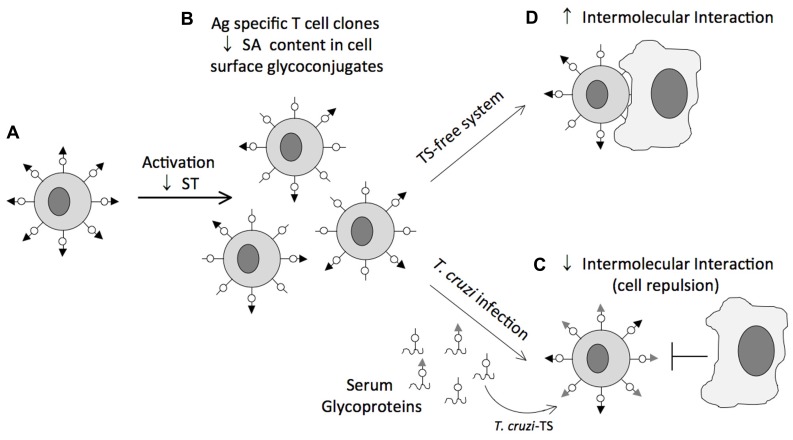
FIGURE 4.
Representative scheme of the glycosylation status of CD8+ T cells during T. cruzi infection. Naïve CD8+ T cells are heavily sialylated (A). During T cell activation, down-regulation of sialyltransferases (ST) renders potential sialic acid acceptors accessible to sialylation through TcTS activity (B). This sialylation may be advantageous to the parasite, because CD8+ T cells resialylated by TcTS present compromised Ag-specific responses since sialic acid charge might increases intercellular repulsion and therefore weakens TCR/MHC class I-mediated cell–cell interactions (C). Absence of TS may favor the TCR/MHC class I cell–cell interaction consequently, development of the immune response (D).