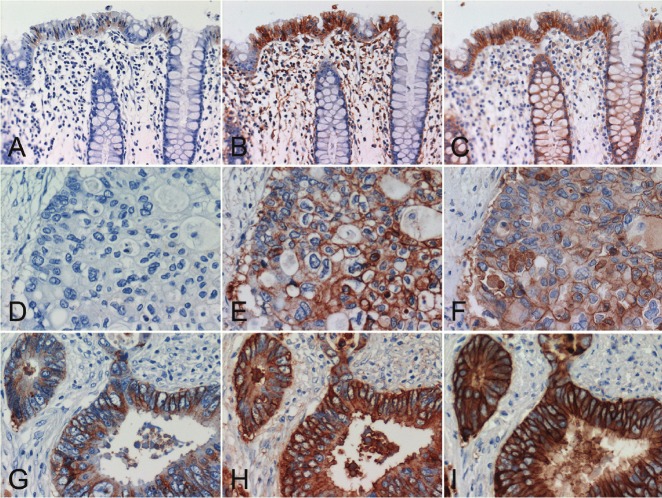
Figure 2.
Comparative study of two colon cancer cases using the standard and modified EGFR PharmDx™ and high-sensitivity EGFR immunostaining with DAK-H1-WT and Novolink. (A, D, G) standard EGFR PharmDx™, (B, E, H) modified EGFR PharmDx™ using CSAII as the secondary reagent, (C, F, I) high-sensitivity EGFR immunostaining with DAK-H1-WT and Novolink. (A, B, C) non-neoplastic crypt epithelial cells, (D, E, F, G, H, I) advanced colorectal carcinomas. The top panels (A-C) and middle panels (D-F) were sampled from the same case. In the normal region shown in the top panels (A-C), 1+ signals are obtained with the standard EGFR pharmDx™, and 3+ reactivities are appreciated many of non-neoplastic crypt epithelial cells in the modified EGFR PharmDx™ and high-sensitivity EGFR immunostaining. In the lesion indicated in the middle panels (D-F), no positivity is seen with the standard EGFR PharmDx™, while the modified EGFR PharmDx™ and high-sensitivity EGFR immunostaining result in strong reactivity in a large number of cancer cells. In the lesion demonstrated in the bottom panels (G-I), 3+ signals are obtained with the standard EGFR PharmDx™, and diffuse and very strong membrane plus cytoplasmic reactivities are seen with the modified EGFR PharmDx™ and high-sensitivity sequence. Stromal deposition of the reaction product is seen in case of the modified PharmDx™.