Figure 4.
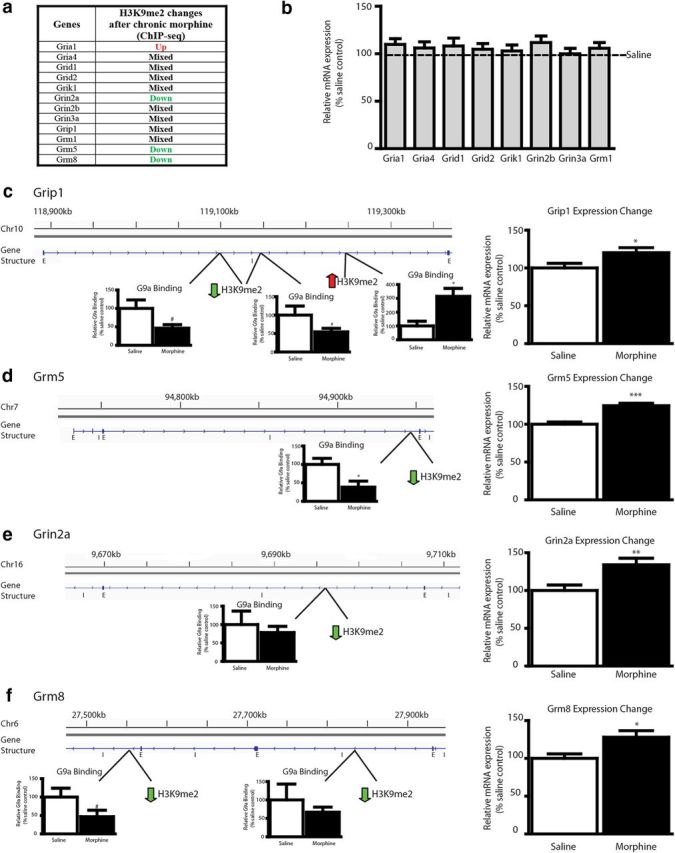
Chronic morphine regulates H3K9me2 and G9a binding at, and expression of, glutamate receptor genes. a, Summary of glutamate signaling genes that were regulated in H3K9me2 binding after chronic morphine treatment, as analyzed by ChIP-seq results. b–f, All glutamatergic-associated genes displaying differential H3K9me2 enrichment after chronic morphine were studied for expression changes after morphine treatment by qPCR in independent tissue samples. b, Several genes in a, which did not show concerted changes in H3K9me2, did not show altered mRNA expression levels. The exception was grip1 (c), which showed an increase in expression after morphine treatment. In contrast, the three genes in a that did display concerted changes in H3K9me2 also show commensurate changes in mRNA expression levels (d–f). Most of these latter genes also exhibited equivalent changes in G9a binding. Representative areas along the gene in which H3K9me2 and corresponding G9a binding changes after morphine treatment are shown in c–f. E, Exons; I, introns. Student's t tests were performed for qPCR validation and G9a ChIP between saline- and morphine-treated animals. #0.05 < p < 0.1, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
