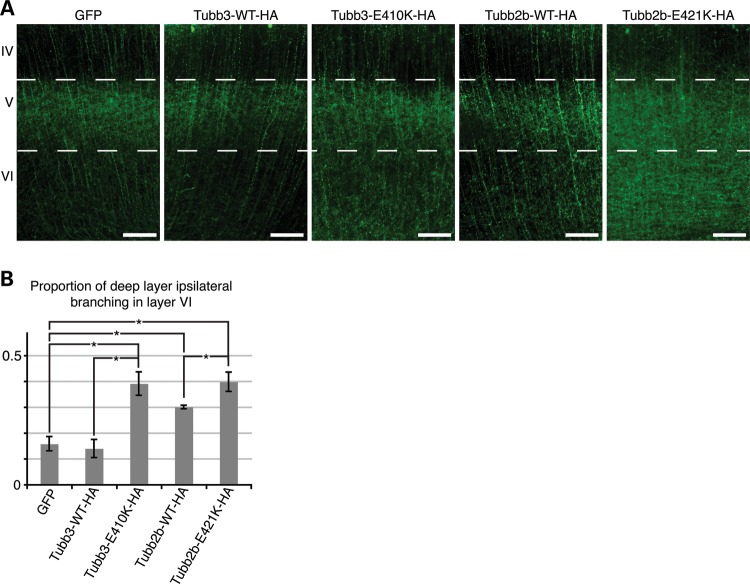
Figure 6.
Tubb2b-E421K-HA alters the layer specificity of local branching. Fluorescent micrographs of CPN electroporated at E15.5 and analyzed at P6. (A) Axons of CPN expressing GFP, Tubb3-WT-HA, or Tubb2b-WT-HA have sent dense interstitial branches into layer V of the ipsilateral cortex, but few branches into the deeper layer VI. In contrast, axons of CPN expressing Tubb3-E410K-HA and Tubb2b-E421K-HA do not show similar specificity as a high density of branching is seen in layer VI, in addition to layer V. (B) Quantitative analysis of the fluorescence intensity in the deep layers (V and VI) reveals that 0.16 ± 0.03 of GFP, 0.14 ± 0.04 of Tubb3-WT-HA and 0.30 ± 0.01 of Tubb2b-WT-HA branches target layer VI. Tubb2b-WT-HA electroporation significantly increases the proportion of layer VI branching (P < 0.01 compared with GFP). There is, however, also a significant increase in the proportion of branching in layer VI in both mutant conditions, with 0.39 ± 0.05 of Tubb3-E410K-HA (P < 0.01 compared to Tubb3-WT-HA control) and 0.40 ± 0.04 of Tubb2b-E421K-HA (P < 0.05 compared with Tubb2b-WT-HA control) branching in layer VI. n = 4 (GFP), n = 3 (Tubb3-WT-HA), n = 3 (Tubb3-E410K-HA), n = 5 (Tubb2b-WT-HA), n = 4 (Tubb2b-E421K-HA). Each n represents one embryo. One-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey t-test was used for multiple comparisons. IV, neocortical layer IV; V, neocortical layer V; VI, neocortical layer VI. Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05. Scale bars: 100 µm.