Figure 4.
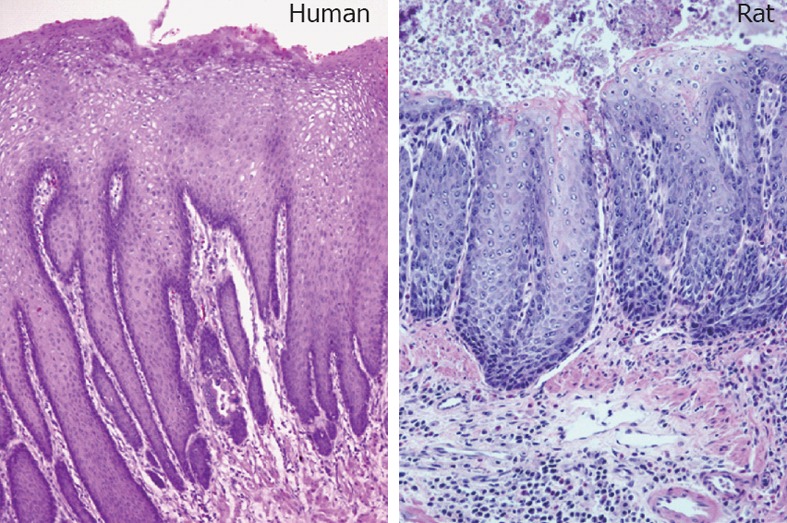
Gastroesophageal reflux disease-induced esophagitis in human and rat (hematoxylin and eosin staining). Gastroesophageal reflux disease rats were created by surgically anastomosing the duodenum to the gastroesophageal junction. These rats can develop esophageal adenocarcinoma within a year, in a pathological sequence similar to human esophageal malignancy.
