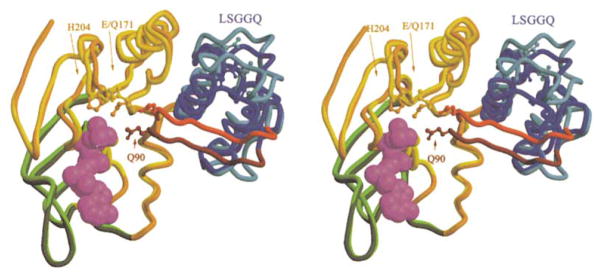
Figure 4. Conformational Differences between ADP-Bound and ATP-Bound MJ0796 Monomers.
The crystal structure of Mg-ADP-bound wild-type MJ0796 (Yuan et al., 2001) (lighter colors) is superimposed on that of the Na-ATP-bound E171Q mutant (darker colors) based on least-squares alignment of 65 Cα atoms located in the α helix following the Walker A motif and the 6 β strands in the F1-type ATP binding core. The backbone and sidechains of each model are color coded according to subdomain organization as in Figure 2A. The crystal structure of the E171Q mutant of MJ0796 bound to Mg-ADP is essentially identical to that of the wild-type protein bound to the same ligand (data not shown). This view shows the molecular surface of the monomer facing the intersubunit interface in the nucleotide sandwich dimer.