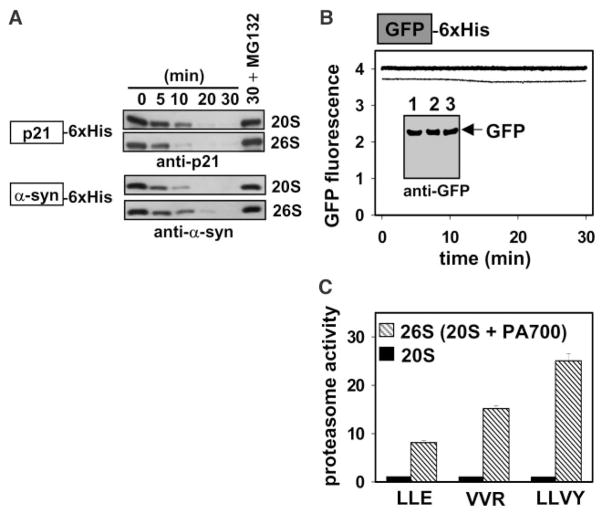
Fig. 1.
Proteasomal degradation of natively disordered substrates. (A) For p21 degradation, 400 nM p21 was incubated with 5 nM latent 20S or active 26S proteasome at 37°C in buffer A [20 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.1; 200 mM NaCl; 10 mM MgCl2; 0.25 mM adenosine triphosphate (ATP); and 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT)]. For α-syn degradation, 500 nM α-syn was incubated with 10 nM latent 20S or active 26S proteasome at 37°C in buffer B (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.1; 20 mM NaCl; 10 mM MgCl2; 0.25 mM ATP; and 1 mM DTT). The degradation time course was monitored by immunoblotting with monoclonal antibodies to p21 or α-syn. 6XHis indicates the hexameric histidine metal affinity tag. 30+ MG132 represents the thirty minute time point in the presence of the proteasome inhibitor. (B) 100 nM GFP was incubated with 20 nM 20S or 26S proteasome at 37°C in buffer B. The stability of GFP was assessed by continuously monitoring fluorescence (λex/em = 395/508 nm; +20S, thin trace; +26S, thick trace) and by immunoblotting (inset) with an antibody to GFP at the beginning (lane 1) and on completion of fluorescence monitoring (+20S, lane 2; +26S, lane 3). (C) The latency of the 20S proteasome (black bars) was assessed by comparing its multiple catalytic activities to the activated 26S proteasome (hatched bars) with the use of fluorogenic peptide substrates Z-Leu-Leu-Glu-βNA (LLE, capase-like activity), Z-Val-Val-Arg-AMC (VVR, trypsin-like activity), and suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC (LLVY, chymotrypsin-like activity) (14), where Z is benzyloxycarbonyl, βNA is 2-napthylamine, AMC is 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin, and suc is succinyl.