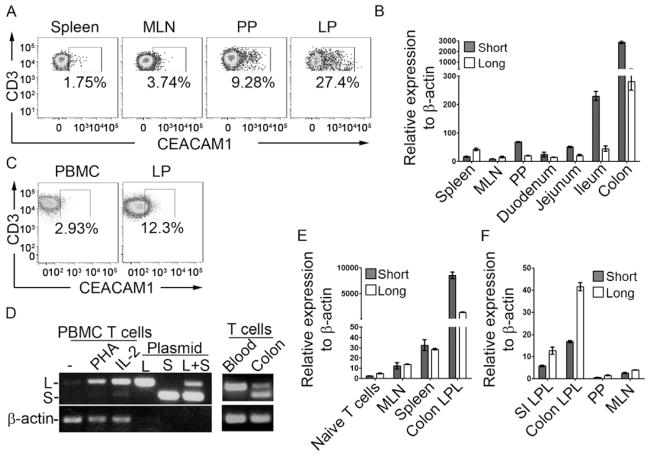
Figure 1.
Intestinal T cells predominantly express CEACAM1-S isoforms. (A) Cell surface expression of CEACAM1 (CC1 antibody) on CD3+ T cells from spleen, MLN, PP or lamina propria (LP) of colon from C57BL/6 mice. (B) qPCR for transcriptional analysis of CEACAM1-L and -S in CD3+ T cells isolated from spleen, MLN, blood, PP or segments of small intestine and colon LP from WT mice. (C) Cell surface expression of CEACAM1 (5F4 antibody) on CD3+ T cells from human peripheral blood (PBMC) or colon LP. (D) Semi-quantification of the relative transcription of CEACAM1-L and -S in human CD3+ T cells isolated from peripheral blood with indicated treatment or from fresh colon LP. (E) qPCR for quantification of CEACAM1-L and -S transcription in naïve CD3+ T cells from WT mice, MLN T cells from WT mice and CD3+ T cells isolated from spleen and colon LP of Rag2−/− mice adoptively transferred with WT CD4+ naïve T cells. (F) T cells isolated from mouse LP were expanded with ConA and IL-2 in vitro for two weeks and the expression of CEACAM1-L and -S were determined by qPCR.