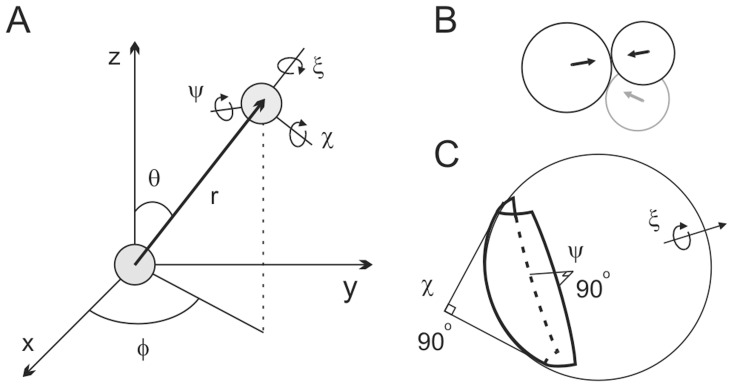
Figure 1. Illustration of the conformational search used in this work.
(A) Definition of the search space in the spherical coordinates. Proteins' CMs are shown as grey spheres, one of which is at the origin of the coordinate system. The moving protein (typically Cc) possesses three translational (θ, φ, r) and three rotational (χ, ψ, ξ) degrees of freedom. For the definition of the rotational axes see text. (B, C) Conformational search in the reduced rotational space. (B) Cc in the starting structure (black circles) is rotated to obtain the shortest separation between the ET cofactors (arrows). This ensures the frontal orientation of the Cc heme during subsequent θ and φ rotations (grey circle). (C) The reduced rotational space −45°≤χ, ψ≤45° traced by a point on the surface of a sphere (bold shape). Location of the other rotation axis, ξ, is indicated.