Figure 2.
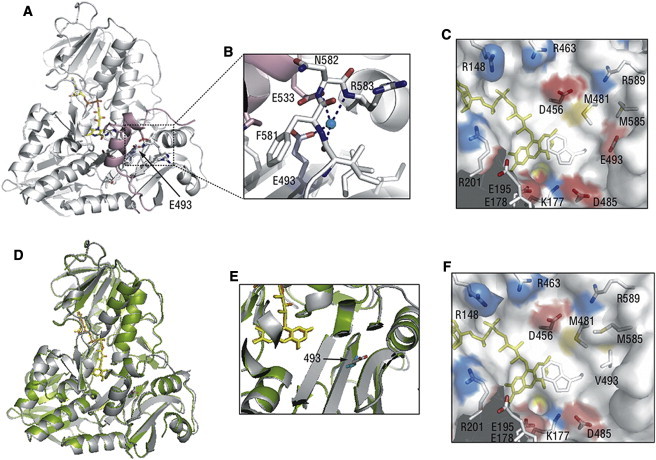
Structural Comparison of the Wild-Type and p.Glu493Val Mutant of AIF
The p.Glu493Val substitution was introduced into the human AIF1 expression plasmid by Stratagene QuikChange kit. Expression, purification, and removal of the C-terminal six-histidine affinity tag were carried out as described previously.18
(A) Position of Glu493 (indicated by an arrow) in oxidized human AIFwt (PDB code 1M6I). FAD is shown in yellow and a partially disordered regulatory peptide is in pink.
(B) Water-bridged contacts involving Glu493 hold the 512–533 helical fragment of the regulatory peptide (pink) close to the active site.
(C) Charge distribution near the flavin cofactor. Positively and negatively charged residues are depicted in blue and red, respectively. Glu493 is 10 Å away from FAD and is part of an acidic cluster adjacent to the isoalloxazine ring.
(D) Superposition of the structures of the wild-type (gray, PDB code 1M6I) and Glu493Val mutant of human AIF (green, PDB code 4FDC). The structure of AIFE493V was solved at 2.4 Å resolution. Data collection and refinement statistics are given in Table S1. The valine side chain is shown in cyan.
(E) A magnified view at the region of AIF near the site of the p.Glu493 residue demonstrating that the substitution does not alter the structure near the active site of AIF.
(F) The Glu493Val substitution changes both the surface profile and electrostatic potential, which may affect solvent accessibility and redox properties of FAD.
