Figure 2.
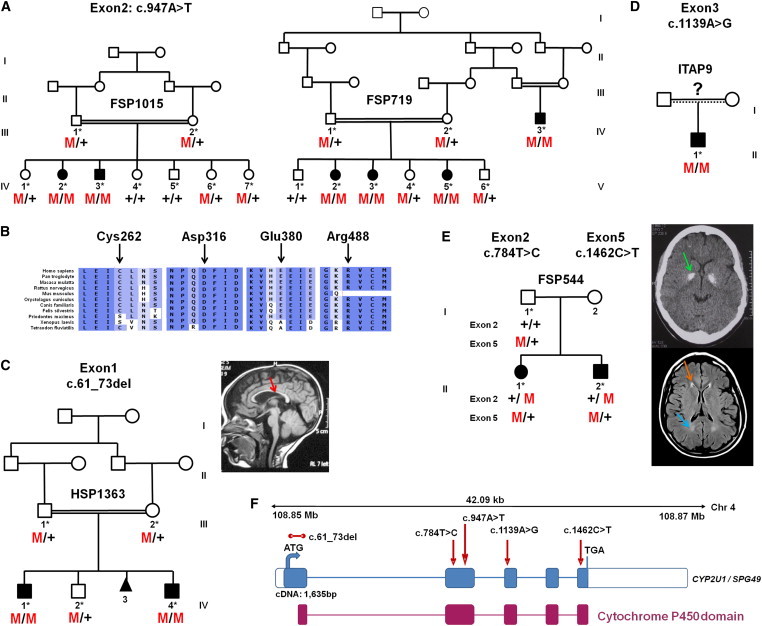
CYP2U1 Mutations in SPG49-Affected Subjects
(A) Segregation analysis of the c.947A>T mutation in two Saudi Arabian families. Their corresponding electrophoregrams are in Figure S2.
(B) Conservation of the amino acids affected by missense variations with the use of ALAMUT software.
(C–E) Pedigrees and segregation of mutations in AR-HSP-affected families HSP1363 (C), ITAP9 (D), and FSP544 (E). A T1-weighted sagittal cerebral MRI from individual HSP1363-IV.4 shows a thin corpus callosum (C, red arrow). A CT scan of individual FSP544-III.1 (E, top view) shows bilateral globus pallidus calcifications (E, green arrow), and a brain MRI (E, bottom view) shows white-matter abnormalities (E, blue arrow), including the “ear of the lynx” aspect of frontal horns of the lateral ventricles (E, orange arrow).
(F) Schematic representation of CYP2U1 (coding exons are represented by blue boxes). The locations of the identified mutations (c.61_73del [p.Leu21Trpfs∗19], c.784T>C [p.Cys262Arg], c.947A>T [p.Asp316Val], c.1139A>G [p.Glu380Gly], and c.1462C>T [p.Arg488Trp]) are shown with red arrows, and the cytochrome P450 domain is indicated by red boxes. The five exons of CYP2U1 (RefSeq NM_183075.2) cover 1,635 bp and encode a 544 amino acid protein with potential transmembrane domains and a heme binding site in the cytochrome P450 domain.
