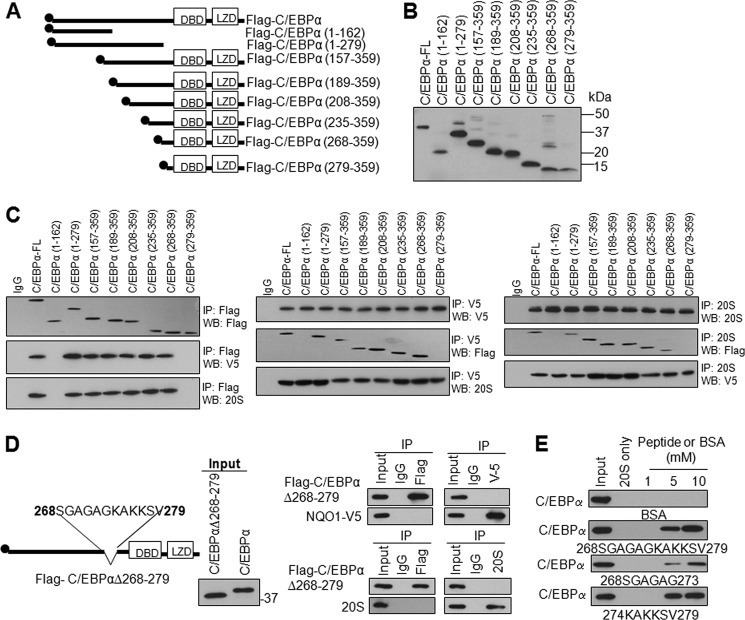
FIGURE 3.
C/EBPα domain between S268 and V279 is required for its interaction with both NQO1 and 20S in HL-60 cells. A, schematic domain structure of C/EBPα and its truncated mutants. DBD, DNA binding domain; LZD: leucine zipper region, and 2×Flag-tag are indicated. B, input for co-immunoprecipitation. Flag-tagged wild type and mutant C/EBPα plasmids were transfected into HL-60 cells, 80 μg cell lysates were loaded and separated on 12.5% SDS-PAGE, and probed with anti-Flag antibody. C, C/EBPα S268-V279 domain is required for interaction with both NQO1 and 20S. HL-60 cells were co-transfected with full-length or truncated mutant Flag-C/EBPα and NQO1-V5, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies as indicated, immunoblotted, and probed with anti-Flag, anti-V5, and anti-20S antibodies as shown. D, internal deletion of S268-V279 domain from C/EBPα leads to loss on interaction of C/EBPα with NQO1 and 20S. HL-60 cells were transfected with full-length or internal deletion mutant of Flag-C/EBPα and NQO1-V5, lysed, immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotted. Immunoblot was probed with anti-Flag and anti-V5 antibodies (right upper panels), or probed with anti-Flag and anti-20S antibodies (right lower panels). E, in vitro translated wild type C/EBPα is incubated with purified 20S proteasomes in absence and presence of the synthesized peptides C/EBPα (S268-V279, S268-G273, and K274-V279) for 2 h and analyzed by immunoblotting and probing with anti-C/EBPα antibody. Molecular weight markers are shown on the right side of panels. All input were 10% of the proteins used in the experiments.