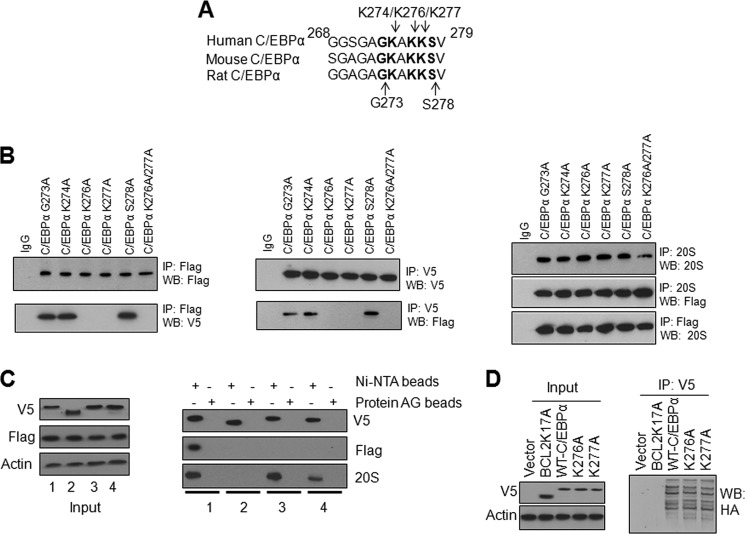
FIGURE 4.
Lysine 276 and lysine 277 of C/EBPα play critical roles in interaction with NQO1. A, alignment of C/EBPα domain S268-V279 from human, mouse, and rat. B, mutation of K276 and K277 to alanine in C/EBPα causes the loss of interaction with NQO1 but not with 20S. HL-60 cells were co-transfected with mutant Flag-C/EBPα and NQO1-V5, lysed, and immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted as shown. C, His-tagged-C/EBPα but not His-tagged-C/EBPα–Δ268–279 deletion mutant pulls down NQO1 and 20S while C/EBPα K276A andC/EBPα K277A mutants pull down 20S and not NQO1. HL-60 cells were co-transfected with Flag-NQO1 and C/EBPα-V5-His-tagged plasmid or C/EBPα mutant plasmids for 48 h. 1 mg cell lysates were pulled down using protein AG or Ni-NTA beads and immuneblotted with anti-V5, Flag, or 20S antibodies. 1: Flag-NQO1+C/EBPα-V5-His6; 2: Flag-NQO1+deletion mutant C/EBPαΔ268–279-V5-His6; 3: Flag-NQO1 +C/EBPαK276A -V5-His6; 4: Flag-NQO1+mutant C/EBPαK277A-V5-His6. D, K276 and K277 are not the ubiquitination sites of C/EBPα. HL-60 cells were co-transfected with HA-Ub and ubiquitination mutant Bcl2K17A-V5, WT C/EBPα-V5 or C/EBPα K276A-V5 or C/EBPα K277A-V5 and 1 mg cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 antibody and probed with anti-HA antibody. All input were 10% of the proteins used in the experiments.