FIGURE 3.
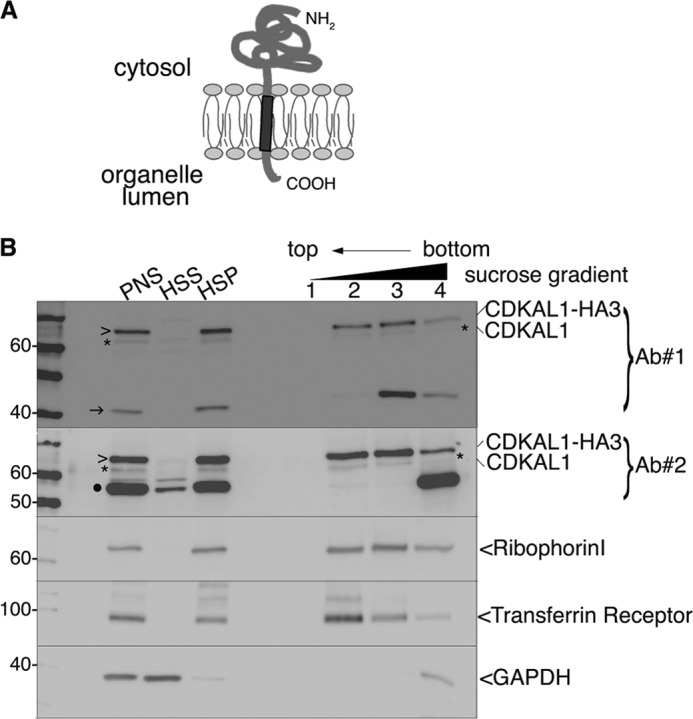
Tight association of CDKAL1 with intracellular membranes. A, schematic representation of the membrane topology of a TA protein. The single TMD (dark gray) at the C terminus is followed by only a few residues in the lumen of the organelle. B, immunoblot analysis of fraction separated by flotation through an alkaline sucrose density gradient. Homogenates from CDKAL1-HA3-transfected INS-1 cells were separated into high speed supernatant (HSS) and HSP fractions. The HSP was treated with Na2CO3 and loaded at the bottom of a discontinuous alkaline sucrose gradient. Membrane vesicles float to the top fractions of the gradient. Both anti-CDKAL1 Ab1 and Ab2 (Ab#1 and Ab#2) were used (top two panels). Ribophorin I and transferrin receptor are control integral membrane proteins; GAPDH is a control soluble cytosolic protein. Endogenous CDKAL1 (*) and transfected CDKAL1-HA3 (>) display an overlapping distribution profile, similar to the ones of control membrane proteins. Note that both the 40-kDa (→) and 55-kDa (●) proteins detected with anti-CDKAL1 antibodies are restricted to the bottom of the gradient, implying only a peripheral or indirect association with membranes. PNS, post-nuclear supernatant.
