FIGURE 1.
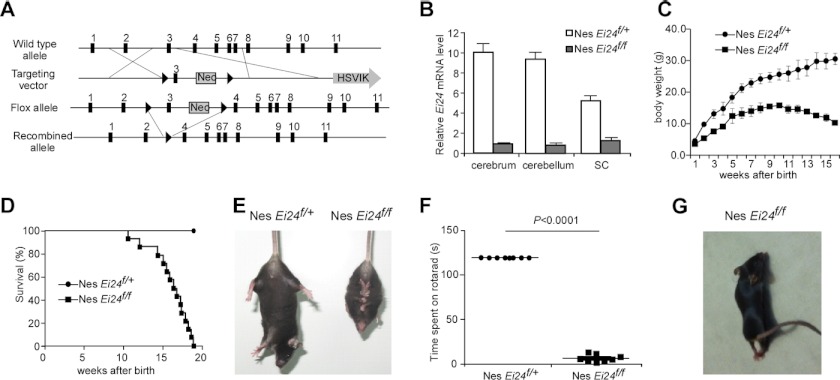
Motor and behavioral deficits in Ei24flox/flox; nestin-Cre mice. A, scheme for generating Ei24 conditional knock-out mice. Exons are depicted by black boxes. A targeting construct was prepared by flanking exon 3 of Ei24 with the neor gene and loxP sites (triangles). The deleted allele of Ei24 was generated by Cre-mediated recombination to remove exon 3. B, Nestin Cre effectively removes exon 3 of Ei24 in brain tissues. Total RNAs were prepared from cerebrum, cerebellum, and spinal cord of Ei24flox/+; nestin-Cre and Ei24flox/flox; nestin-Cre mice at 4 months of age. Transcription levels of Ei24 mRNA are normalized to Actin mRNA. Results are representative of at least three experiments. C, body weight curves of Ei24flox/+; nestin-Cre and Ei24flox/flox; nestin-Cre mice over 16 weeks. Mean ± S.E. of 18 mice is shown. D, survival curves of Ei24flox/+; nestin-Cre (n = 18) and Ei24flox/flox; nestin-Cre mice (n = 18) mice over 19 weeks. E, when lifted by the tail, Ei24flox/+; nestin-Cre mice extend their limbs, while Ei24flox/flox; nestin-Cre mice have an abnormal limb-clasping reflex, adopting a bat-like posture. F, time spent on an autoaccelerating rod (rotarod). The maximum observed time was 120 s. Mean ± S.E. of 9 mice is shown. G, when Ei24flox/+; nestin-Cre mice initiate movement, their hindlimbs are held in a posteriorly hyperextended position.