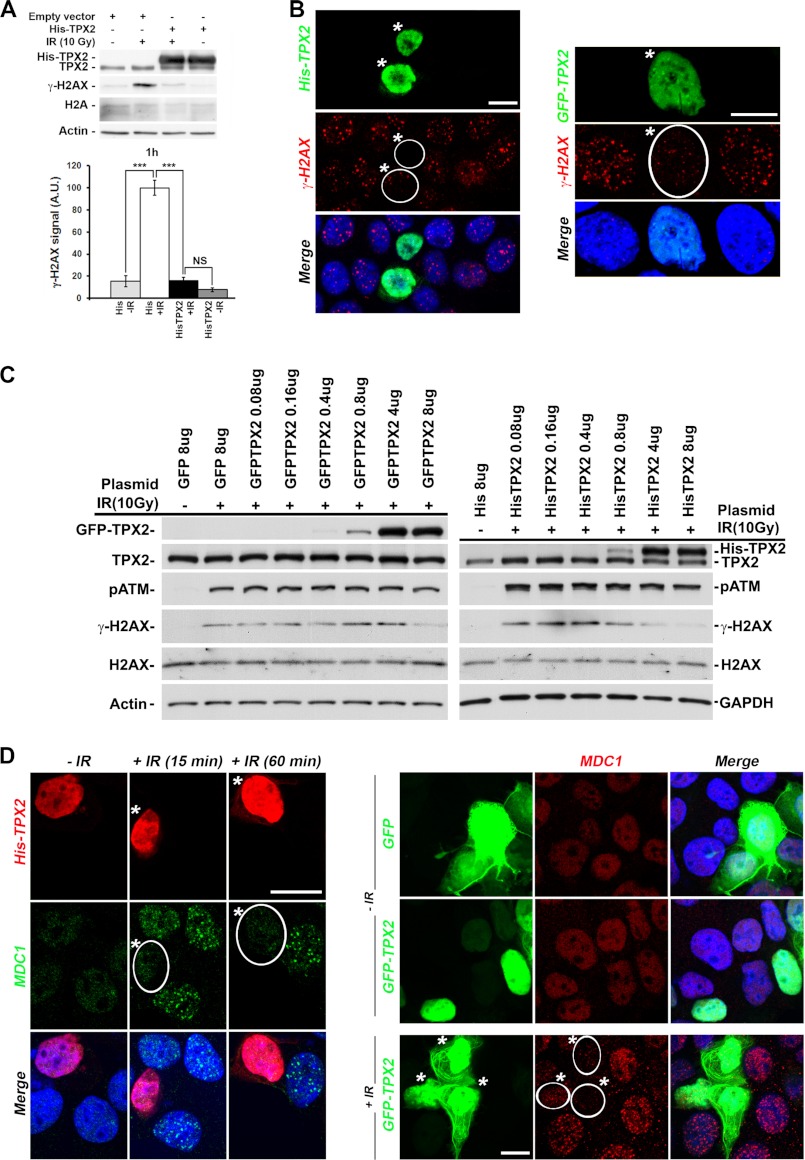
FIGURE 2.
Effects of TPX2 overexpression on the levels of γ-H2AX and MDC1 ionizing radiation-induced foci. A and B, overexpression of His-TPX2 or GFP-TPX2 significantly decreases phosphorylation of H2AX in HeLa (A) and MCF-7 cells (B) 1 h after ionizing radiation treatment as indicated by Western blot analysis (10 Gy) (A) and immunofluorescence microscopy (B) (left panel, 2Gy; right panel, 4Gy). A, relative quantifications of γ-H2AX signals from independent experiments are shown in bar charts: control +IR (100.0 ± 6.9) versus His-TPX2 +IR (16.0 ± 2.9), p < 0.001, n = 4 (independent experiments); group (mean ± S.E.), unpaired t test. Levels of actin and H2A were used as loading controls. NS, non-significant; ***, p < 0.001. Error bars represent S.E. C, dose-dependent effects of GFP-TPX2 or His-TPX2 on the levels of ionizing radiation-induced γ-H2AX. The amount of plasmid transiently transfected per 6-cm cell culture dish is indicated. Proteins on Western blots were visualized with the indicated antibodies. TPX2 antibodies recognize endogenous and exogenous TPX2 on the same Western blot, thereby allowing comparison of absolute protein levels (see text for details). D, overexpression of His-TPX2 or GFP-TPX2 inhibits MDC1 ionizing radiation-induced focus formation in MCF-7 cells after 2 or 4 Gy (15-min recovery), respectively. Bar in B and D, 10 μm. Merged images include DAPI staining (B and D). A.U., arbitrary units. Transfected cells are indicated by white frame and asterisks (B and D).