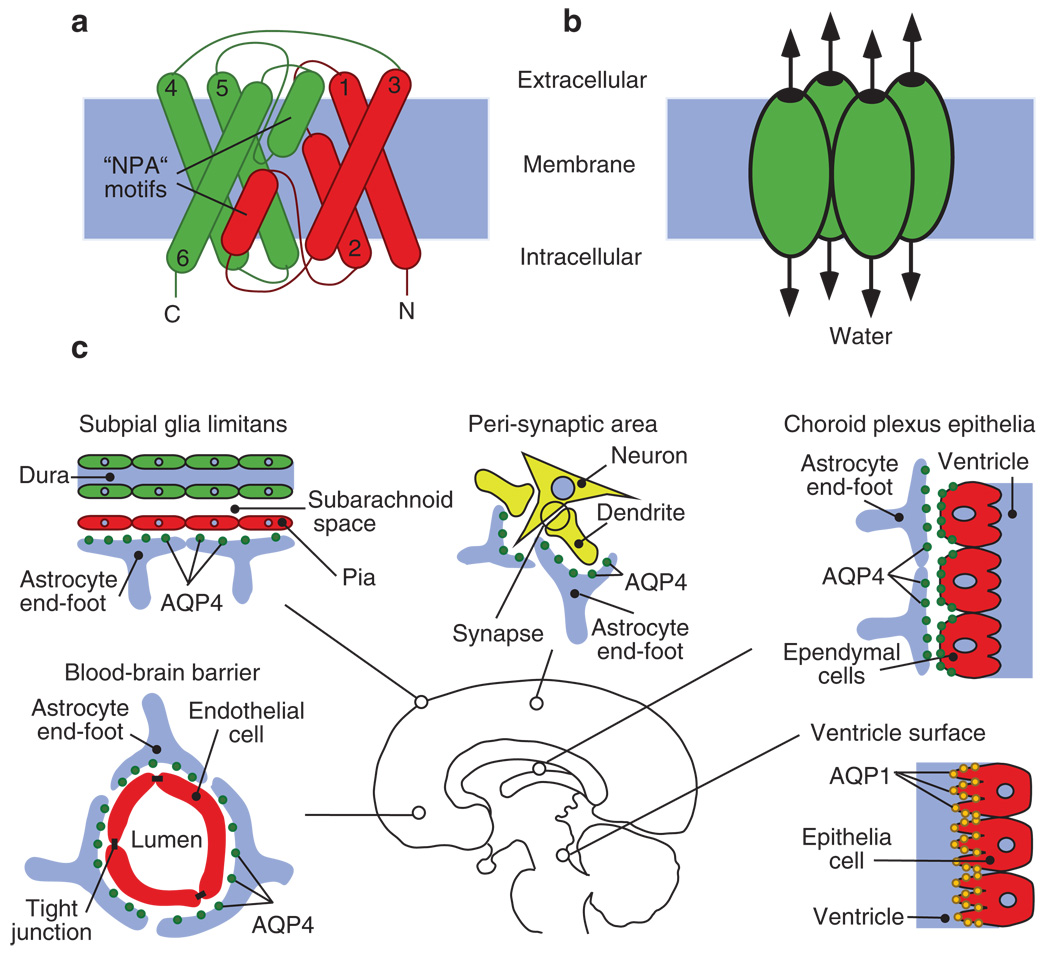
Fig. 1.
(a, b) Diagram depicts the structure of an AQP monomer and its clustering into tetramers. (a) Schematic demonstration of the transmembrane α-helices of AQP4 numbered from 1–6, which surround the highly selective water pore. The highly conserved “NPA” motifs are indicated. (b) AQP organizes into tetramers in the cell membrane with each unit functioning as an independent pore. (c) The distribution of CNS AQPs. AQP4 is polarized at the glial end-feet facing CSF–brain, blood–brain barrier and peri-synaptic areas. Ependymal cells have basolateral expression of AQP4. The apical processes of the choroid plexus cells are rich in AQP1 expression (adapted from Zador and Manley 2008)