FIGURE 1. Analysis of LCMT-1 knockdown and PP2A methylation in LCMT-1 shRNA HeLa cells.
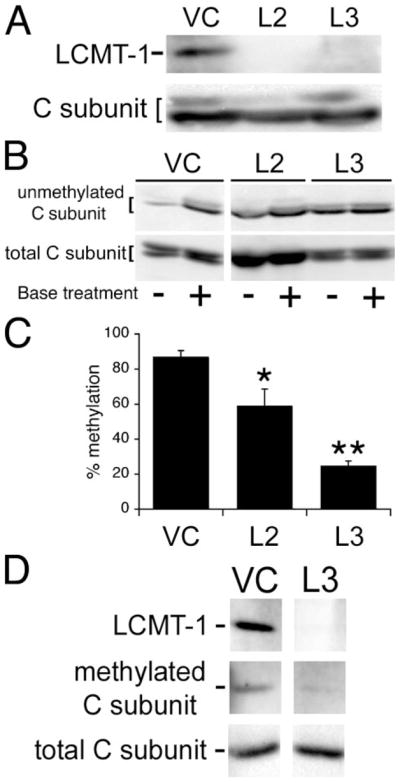
A, two different LCMT-1 shRNAs (L2 and L3) efficiently knockdown LCMT-1 protein levels in HeLa cells. VC cells and cells stably expressing the L2 and L3 LCMT-1 shRNAs were lysed, and lysates were probed for the steady-state levels of LCMT-1 and PP2A C subunit (C subunit; loading control) by immunoblotting. B, knockdown of LCMT-1 by expression of L2 or L3 shRNAs reduces PP2A C subunit methylation in HeLa cells. VC cells and LCMT-1 L2 and L3 shRNA cells were lysed, and the steady-state level of PP2A methylation in each cell line was determined using our previously published assay (24). Briefly, because base treatment demethylates the PP2A catalytic subunit, one aliquot of lysate from each line was treated for 5 min at 4 °C with 0.2 N NaOH to completely demethylate PP2A C subunit and was then neutralized (+lanes; 100% demethylated control), whereas another equal aliquot of lysate from each line was combined with preneutralized buffer (−lanes reflect endogenous methylation level). Then the untreated and base-treated aliquots were analyzed side by side on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel followed by immunoblotting with a monoclonal antibody (4b7) specific for unmethylated C subunit. Demethylation of PP2A C subunit induced by L2 and L3 shRNA expression can be seen as an increase in the relative intensity of 4b7 signal in the minus versus plus lanes as compared with vector control cells. Also shown is an immunoblot of total PP2A C subunit showing that each pair of − and +lanes was loaded equally. C, the percent unmethylated PP2A catalytic subunit was determined by quantitatively comparing the amount of 4b7 signal in untreated samples (reflects level of endogenous unmethylated PP2A C subunit in each line) to that in the matched base-treated samples (100% demethylated controls) using a Bio-Rad Fluor-S Max Chemilumimager. Percent methylation was calculated by subtracting the percent of unmethylated PP2A from 100. The graph shows the averages and S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significance versus vector control as assayed by t test (*, p = 0.0499; **, p = 0.0001). The C subunit can migrate as either singlets or doublets; whether double or single bands are seen can vary for the same sample from gel to gel. This pattern of migration in SDS-PAGE has been noted previously for endogenous PP2A C subunits (6, 8, 24, 32) and does not appear to be due to degradation. D, immunoblotting with the anti-methylated PP2A catalytic subunit antibody, 2A10, further strengthens the conclusion that LCMT-1 is the major PP2A methyltransferase in vivo. Lysates prepared from VC and L3 LCMT-1 knockdown cells were analyzed by immunoblotting with LCMT-1 antibody to demonstrate LCMT-1 knockdown and with 2A10 monoclonal antibody (methylated C subunit) to show L3 LCMT-1 knockdown causes a substantial reduction in PP2A catalytic subunit methylation. Also shown is an immunoblot of total PP2A C subunit showing that the lanes were loaded equally. Quantitation of the 2A10 signals from two separate experiments showed that there was greater than a 3-fold reduction in methylation in the L3 LCMT-1 shRNA knockdown cells.
