FIGURE 2. LCMT-1 knockdown reduces C subunit-Bα association.
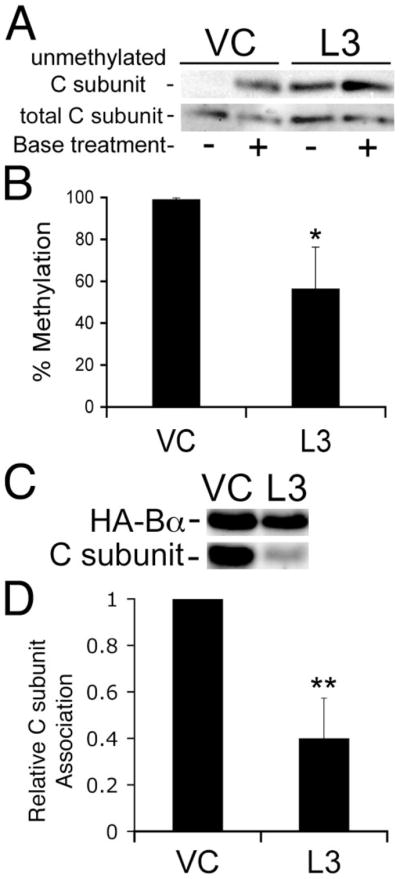
VC cells and cells stably expressing an shRNA directed against LCMT-1 (L3) were transfected with a construct expressing HA-tagged Bα (HA-Bα) or an empty vector. A, the steady-state level of PP2A methylation in VC and L3 lysates (5% of the input of each immunoprecipitate) was determined using our previously described assay using our 4b7 methylation-sensitive monoclonal antibody (see the legend for Fig. 1B). The reduction in methylation induced by expression of the L3 shRNA can be seen by the increased signal in the −lane. Also shown is an immunoblot of total PP2A C subunit showing that each pair of − and +lanes was loaded equally. B, percent methylation of the PP2A catalytic subunit was determined as described in the legend to Fig. 1C. The graph shows the averages and S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments. The asterisk indicates significance versus vector control as assayed by t test (*, p = 0.02). C, HA-Bα immunoprecipitates of VC and L3 shRNA cells were probed for HA-tagged Bα (HA-Bα) and C subunit. The image shown is a representative immunoblot of three independent experiments. D, each band in panel C was quantitated using a Bio-Rad Fluor-S Max Chemilumimager. The relative amount of C subunit bound to HA-Bα (Relative C subunit association) was calculated as a measure of the efficiency of C subunit association with HA-Bα. The graph shown displays the average C subunit association with HA-Bα in the three experiments. Error bars show S.D. of the three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significance versus vector control as assayed by t test (**, p = 0.0038).
