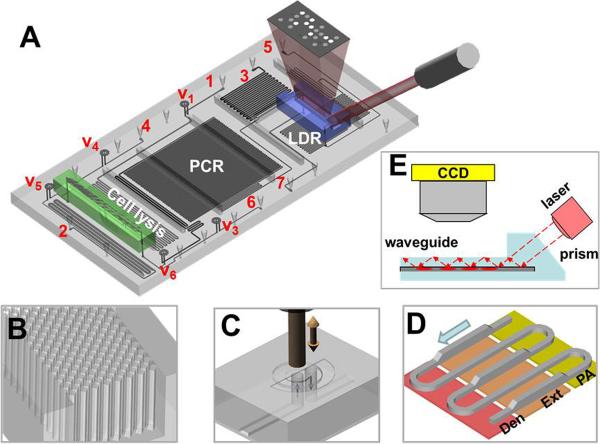
Figure 2.
Integrated, modular fluidic cartridge for TB analysis. (A) 3D rendering of the cartridge and the array. 1–7 - fluidic inlets and outlets: 1 - sample inlet, 2 – PCR cocktail inlet, 3 – LDR cocktail inlet, 4 – ethanol and air inlet, 5 – array wash inlet, 6 – vacuum connection, 7 – waste. V1–V6 – on-chip membrane valves (note that V2 is positioned next to SPE module on the cell lysis microchannel and is not visible in the current view). (B) Close-up of the SPE bed showing DNA capture bed filled with an array of high-aspect ratio pillars. (C) Schematic operation of the on-chip membrane valve with mechanical actuation – electrically actuated solenoid presses on the polymer membrane closing the passage of fluid from the bottom layer through the valve and back to the bottom layer. (D) Geometry of the continuous flow PCR reactor with dual-depth microchannels for extended residence time in the extension-zone; Den – denaturation, Ext – extension, PA – primer annealing. (E) Schematic representation of the detection mode. Laser excitation is coupled to a waveguide through an integrated prism. Light travelling through the waveguide excites the labeled LDR products hybridized to the zip code array spotted on the waveguide surface.