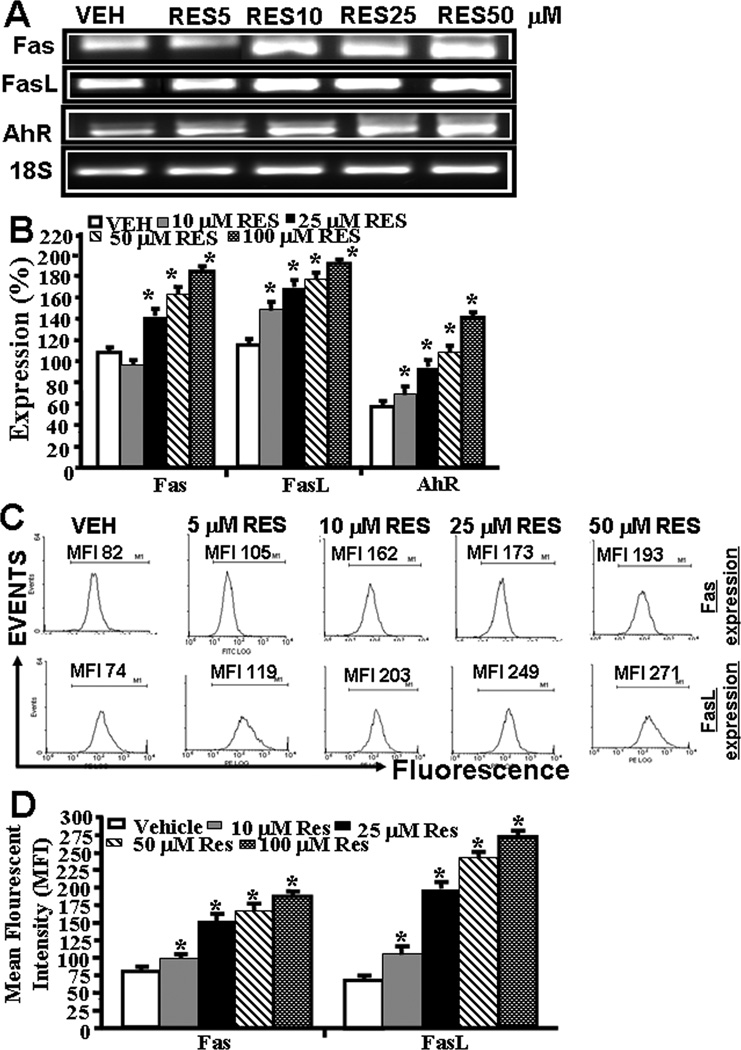
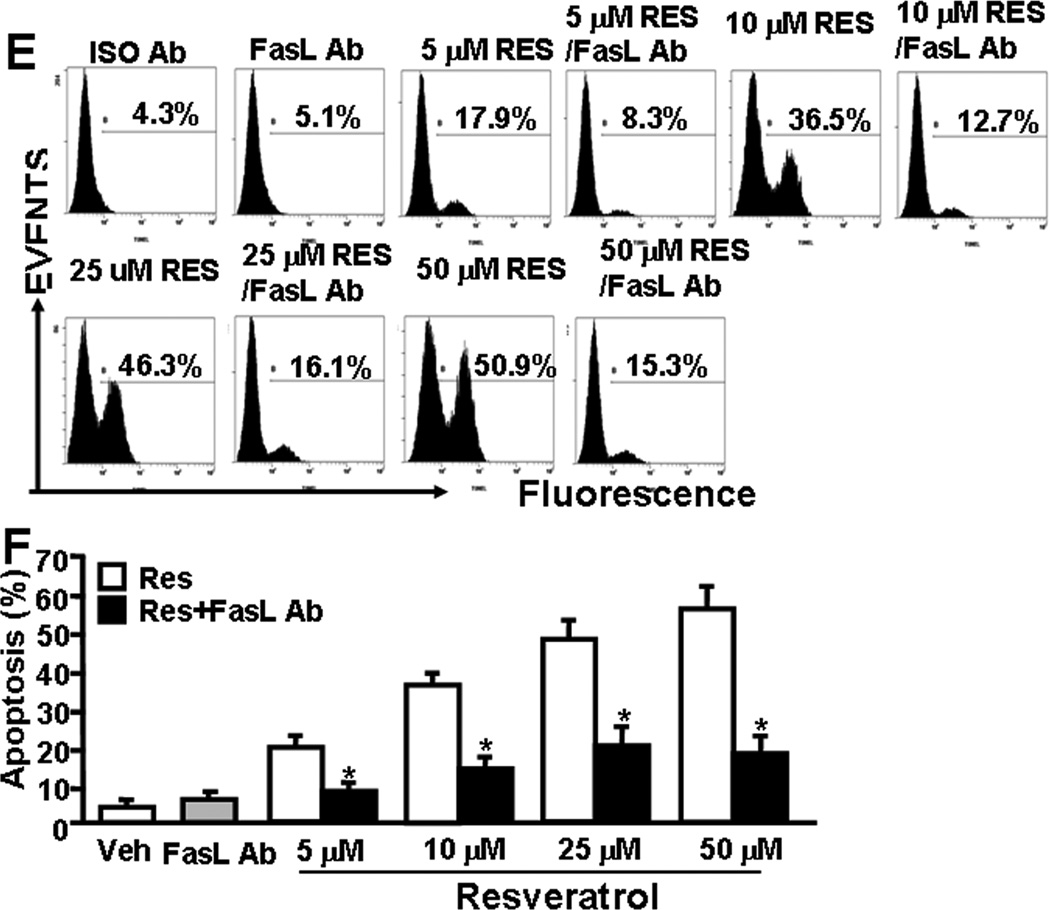
Figure 3.
RES-induced upregulation of AhR, Fas, and FasL in EL4 cells and role of FasL in induction of death-receptor pathway of apoptosis in EL4. Expression of AhR, Fas, and FasL in EL4 cells was determined by performing RT-PCR and staining the cells with anti-mouse Fas-PE and anti-mouse FasL-PE antibodies and analyzed by Flow cytometry. A, Expression of AhR, Fas, and FasL in EL4 cells 24 hrs post RES or vehicle treatment (RT-PCR). 18S, a house keeping, was used as a positive control. B, represents mean ± SEM of three independent experiments and asterisks (*) represent significant (p < 0.05) difference between RES-treated groups when compared to vehicle controls. C, Mean fluorescent intensity of Fas and FasL expression post RES or vehicle treatment. Panel D represents mean ± SEM of three independent experiments and asterisks (*) represent significant (p < 0.05) difference between RES-treated groups when compared to vehicle controls. Panels E and F: Apoptosis in EL4 cells in the absence or presence of mouse-specific anti-FasL Ab was determined by TUNEL assays. The data presented in panel E are representative of 3 independent experiments. Panel F represents mean of 3 independent experiments and asterisks (*) represent significant (p < 0.05) reduction in RES-induced apoptosis of T cells cultured in the presence of FasL Ab when compared to the controls.