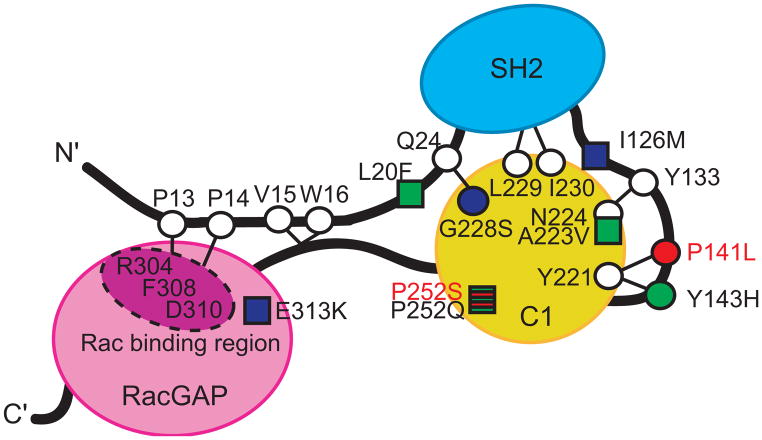
Figure 3. Schematic of α2-chimaerin structure in its closed conformation showing the predicted α2-chimaerin intramolecular interactions.
The three domains of α2-chimaerin are depicted as follows: the N-terminal Src homology-2 (SH2) domain is depicted in blue, the C1 domain that binds to the second message signaling lipid diacylglycerol (DAG) is depicted in yellow; and the RacGAP domain that interacts with Rac and down-regulates its activity is depicted in pink. Linker regions are depicted as black lines. Specific amino acid residues are highlighted as circles or squares, with circles representing the positions of amino acids predicted to be involved in intramolecular interactions that stabilize the closed conformation of α2-chimaerin based on homology with β2-chimaerin.14 The seven previously reported mutations alter amino acid residues that are represented by circles or squares filled with green or blue; those filled with green were previously demonstrated to enhance translocation of α2-chimaerin to the membrane when mutated, while those filled with blue did not.6 The circle filled with red and the square striped red and green represent the residues altered by the new novel mutations: P252S alters the same residue as P252Q (thus the residue is striped), while P14lL alters a residue predicted to interact with Y221. Thus, both residues are anticipated to destablize the closed conformation of α2-chimaerin and result in its pathological hyperactivation. Figure adapted with permission from Miyake et al.6