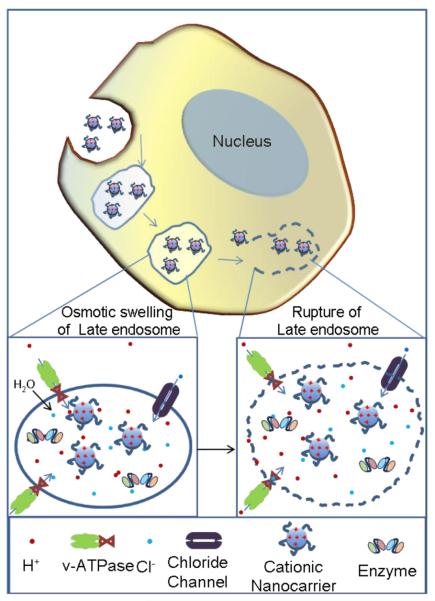
Figure 8.
The proton sponge effect allows for cationic nanoparticles to escape endosomal and lysosomal vesicles and enter the cytoplasm. When cationic nanoparticles enter acidic vesicles, unsaturated amino groups sequester protons supplied by v-ATPase (proton pump). Sequestered protons cause the pump to continue functioning, leading to the retention of chloride ions and water molecules. Eventually, osmotic swelling causes rupture of the vesicle and the cationic nanoparticles are able to enter the cytoplasm.