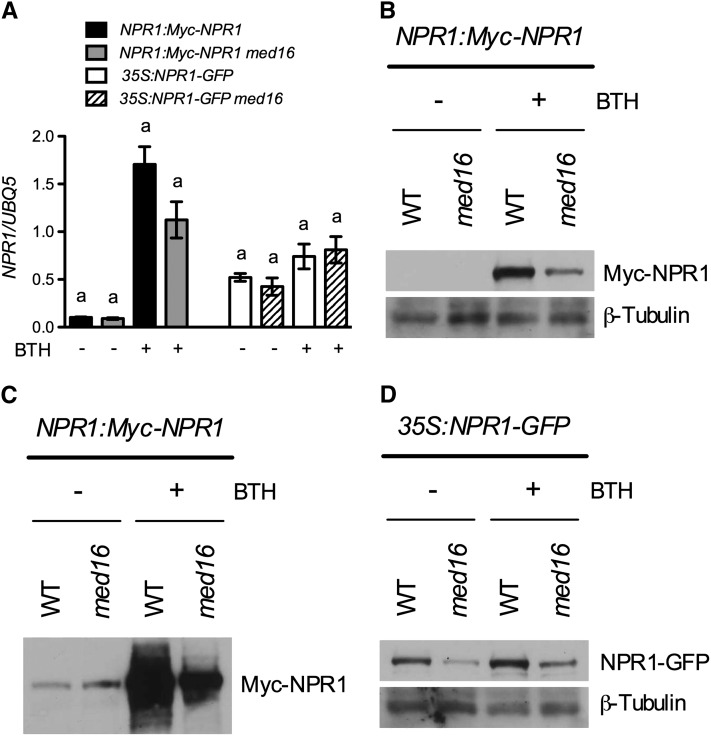
Figure 9.
NPR1 Protein Accumulation in med16 Plants.
(A) Expression levels of NPR1 in NPR1:Myc-NPR1, NPR1:Myc-NPR1 med16-1, 35S:NPR1-GFP, and 35S:NPR1-GFP med16-1 plants treated with or without BTH. Four-week-old soil-grown plants were treated with soil drenches plus foliar sprays of 0.3 mM of BTH solution or water. Leaf tissues were collected 24 h later and subjected to total RNA extraction and real-time qPCR analysis or protein analysis in (B) and (D). Data represent the mean of three independent samples with sd. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05, Student’s t test). The comparison was made separately between NPR1:Myc-NPR1 and NPR1:Myc-NPR1 med16-1 or between 35S:NPR1-GFP and 35S:NPR1-GFP med16-1 for each treatment.
(B) Myc-NPR1 protein levels in NPR1:Myc-NPR1 and NPR1:Myc-NPR1 med16-1 plants treated with or without BTH. Plants were treated as in (A). Total protein was analyzed by reducing SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-Myc antibody. Detection of the constitutively expressed β-tubulin confirmed equal loading. WT, wild type.
(C) Myc-NPR1 protein levels in untreated NPR1:Myc-NPR1 and NPR1:Myc-NPR1 med16-1 plants. A longer exposure of the protein gel blot filter in (B) was used to detect the background protein levels.
(D) NPR1-GFP protein levels in 35:NPR1-GFP and 35:NPR1-GFP med16-1 plants treated with or without BTH. Total protein was analyzed by reducing SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-GFP antibody. Detection of the constitutively expressed β-tubulin confirmed equal loading. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.