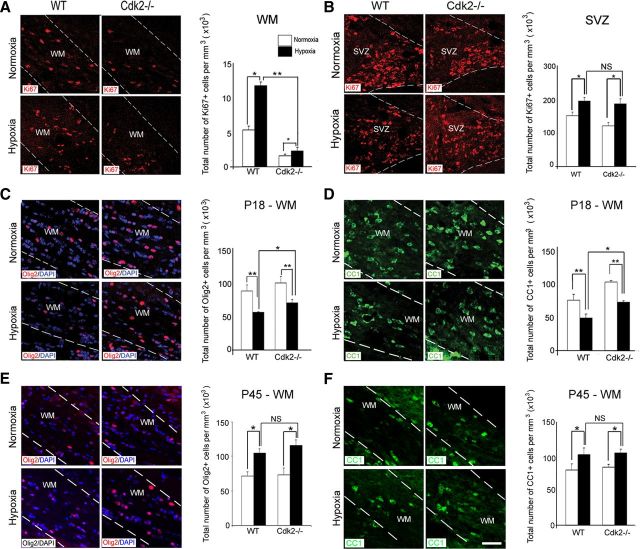
Figure 9.
Cdk2 is essential for oligodendrocyte development after hypoxia. Confocal images of white matter (A) and SVZ (B) from wild-type and Cdk2−/− mice after normoxia and hypoxia at P18. Proliferating cells were labeled with anti-Ki67 antibody. In Cdk2−/− mice, hypoxia caused a modest elevation in proliferation in white matter. A significant proliferative response was also sustained in the SVZ. The dotted lines bound white matter and SVZ. WM, White matter. Scale bar, 30 μm (n = 4 brains for each condition; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.02, two-way ANOVA). Confocal images of immunostaining with Olig2 and CC1 after normoxia and hypoxia at P18 in Cdk2−/− mice and their littermates at P18 and P45. Oligodendrocytes were labeled with Olig2 (C, E) and CC1 (D, F) markers. In wild-type and Cdk2−/− white matter, hypoxia reduced oligodendrocyte differentiation at P18, compared with normoxia, followed by a recovery at P45 (n = 4 brains for each condition, and for each antibody; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.02, two-way ANOVA). Error bars indicate SEM.