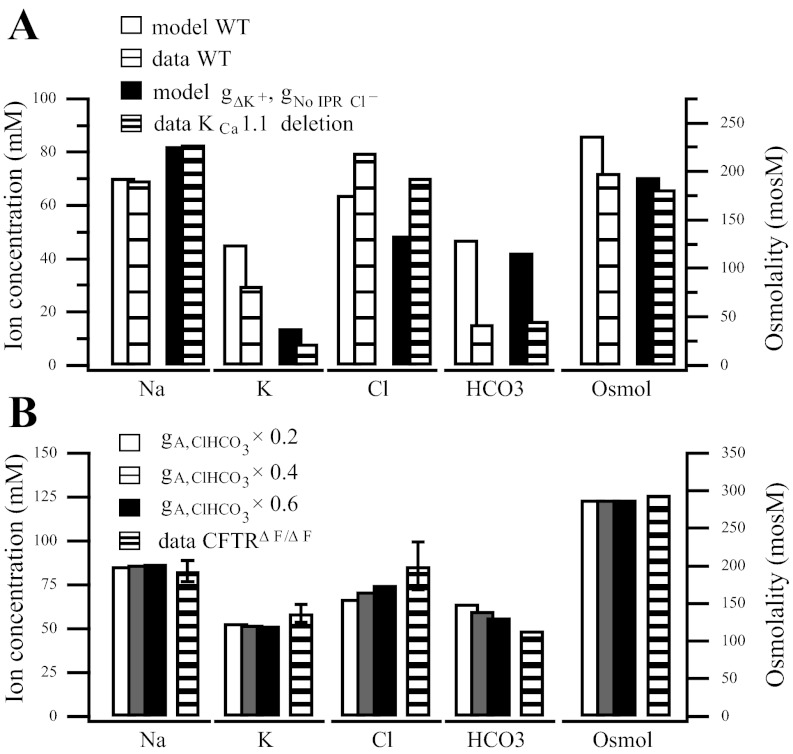
Fig. 4.
A: comparison between our model and the wild-type and KCa1.1 channel deletion final saliva (36). The KCa1.1 channel deletion is represented by a reduction in channel conductance, gΔK+ = 0.01 × gA,K+. We also reduce the CFTR conductance due to the absence of IPR (36), gNo IPR Cl− = 0.5 × gA,Cl−. A further reduction in the channel conductance will raise the final Cl− concentration. B: AE activity is reduced and compared with the CFTRΔF/ΔF mouse. In addition to the parameter modifications in Fig. 3B, the AE activity is also reduced to 60%, gΔClHCO3 = gA,ClHCO3× 0.6 (in black); to 40%, gΔClHCO3 = gA,ClHCO3 × 0.4 (in gray); and to 20%, gΔClHCO3 = gA,ClHCO3× 0.2 (in white). Slight decreases in Cl− and increases in HCO3− occur as the activity is reduced.