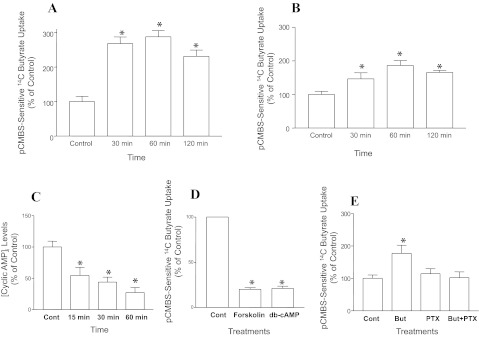
Fig. 1.
Butyrate (But)-induced enhancement of monocarboxylate transporter-1 (MCT1) function is pertussis toxin (PTX)-sensitive and associated with decreased intracellular cAMP levels. {MCT1 function (pCMBS-sensitive [14C]butyrate uptake)} was calculated as nanomols butyrate per milligram protein per 5 min and results are expressed as % of control]. Time-course of butyrate (10 mM) effects on MCT1 function in C2BBe1 cells (14-day postplating) (n = 5, P < 0.05 vs. control) (A) and in IEC-6 cells (10-day postplating) (n = 3, *P < 0.05) (B). Time-course of butyrate (10 mM) effects on intracellular cAMP levels (n = 3, *P < 0.05) (C); forskolin (10 μM) and dibutyryl cAMP (50 μM) effects on MCT1 function (n = 3, *P < 0.001) (D); PTX (1 μg/ml)-sensitivity of butyrate (10 mM) induction of MCT1 function (n = 3, *P < 0.05) (E). pCMBS, p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate.