Figure 2.
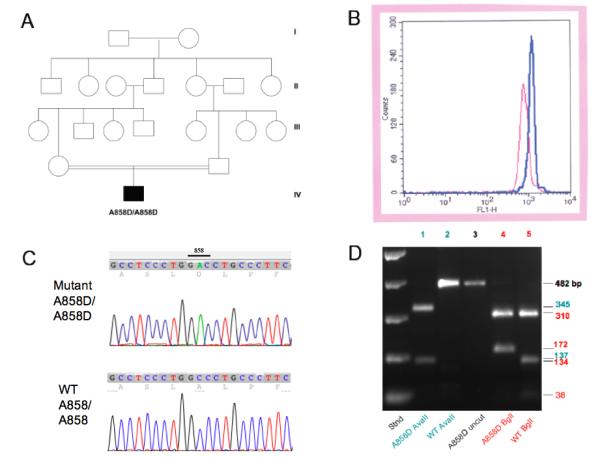
A. Consanguinous pedigree of patient 2. B. Eosin-5′-maleimide surface staining profiles of Patient 2 (red) and of control red cells (red). C. Sequence traces from the AE1 gene exon 19 of Patient 1 (upper) showing the homozygous GCC-GAC mutation encoding the missense substitution A858D, and from a control individual (lower) with the homozygous WT sequence. D. Diagnostic restriction digest of an AE1 gene amplicon from Patient 1 showing acquisition of a novel AvaII site and loss of a BglI site in the mutant allele. The same pattern was noted with genomic DNA from Patient 2 (not shown).
