Figure II.
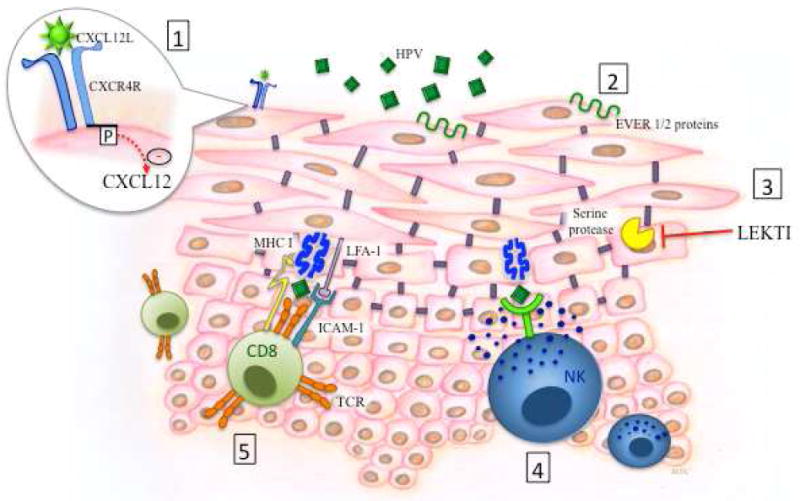
Schematic depiction of the critical elements of host defense against Human Papilloma viruses (HPV) in the skin as determined from primary immune defects.
1. CXCR4: Gain of function mutations inhibit CXCL12 mediated signaling and leukocyte trafficking.
2. EVER 1 and 2: transmembrane proteins that act as restriction factors for HPV.
3. LEKTI inhibits serine protease activity, preventing breakdown of intercellular adhesions. Mutations in SPINK5 lead to decreased LEKTI production and therefore impaired skin integrity.
4, 5. HPV antigen specific activation of natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic CD8 T cells results in degranulation of cytotoxic granules.
