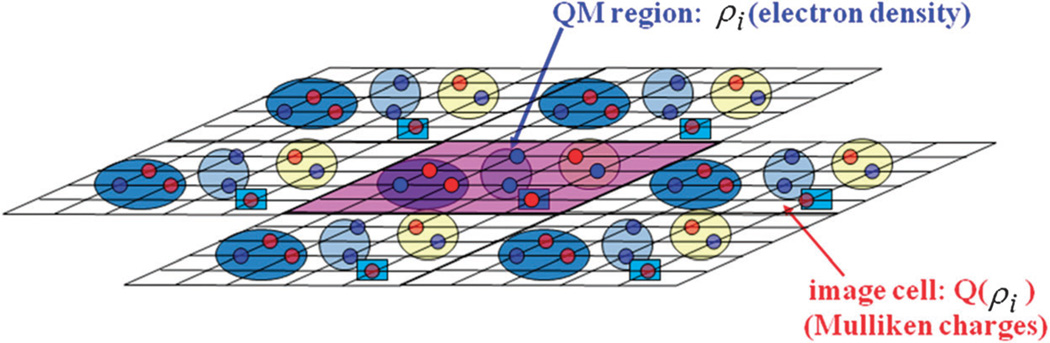
Fig. 1.
Schematic depiction of the X-Pol-Ewald method. Fragments in the primary unit cell are explicitly treated by a quantum mechanical model specified with a smooth charge density ρi, whereas their periodic images are represented by the partial atomic charges derived from the corresponding charge density. In the present study, Mulliken population charges are used to approximate the image charges. Each fragment is specified by a circle or box and all fragments (molecules) in the system are treated by electronic structure theory.