Fig. 6. nElavl-dependent regulation of the brain enzyme glutaminase.
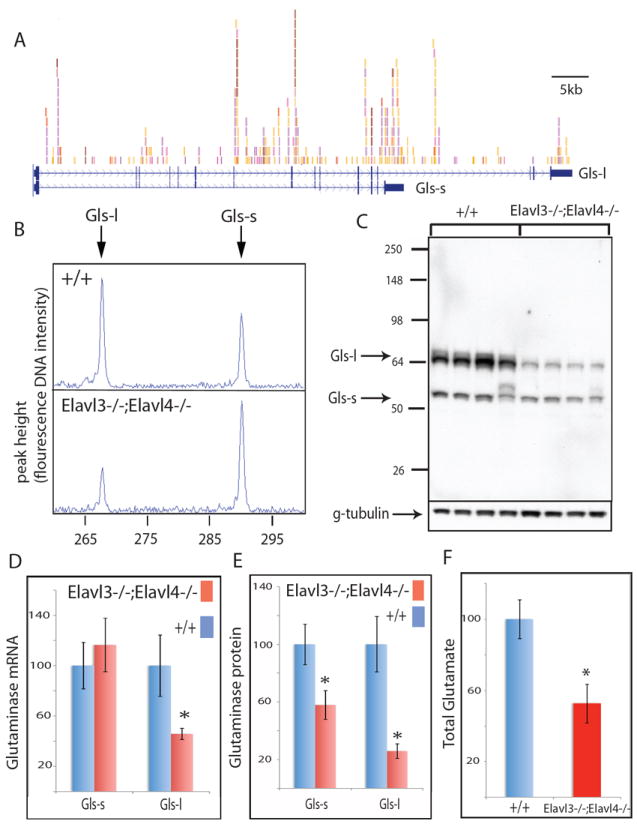
(A) The two mRNA isoforms of the glutaminase gene (Gls) and nElavl binding sites are shown. Individual colors depict different experiments. Alternative use of a 3’ splice site generates two Gls isoforms with different 3’ terminal coding sequences and 3’ UTRs. Gls-s and Gls-l refer to short and long isoforms, respectively. (B) RT-PCR amplification of the two Gls isoforms in WT and Elavl3-/-;Elavl4-/- cortex of age P0 mice. (C) Western blot analysis of the two Gls isoforms in littermate WT and Elavl3-/-;Elavl4-/- cortex of age P0 mice. Each lane represents an independent mouse. (D) Q-PCR quantification of the abundance of two Gls mRNA isoforms in littermate WT and Elavl3-/-;Elavl4-/- cortex of age P0 mice. (E) Quantification of data shown in panel (C). (F) Quantification of total glutamate levels in cortex of 3 WT and 3 Elavl3-/-;Elavl4-/- littermate age P0 mice are presented. Glutamate levels in WT samples are normalized to 100% in the Y-axis. * denotes p<0.01 (t-test). Error bars denote standard deviation. See also Fig.S3-4 and Table S9.
