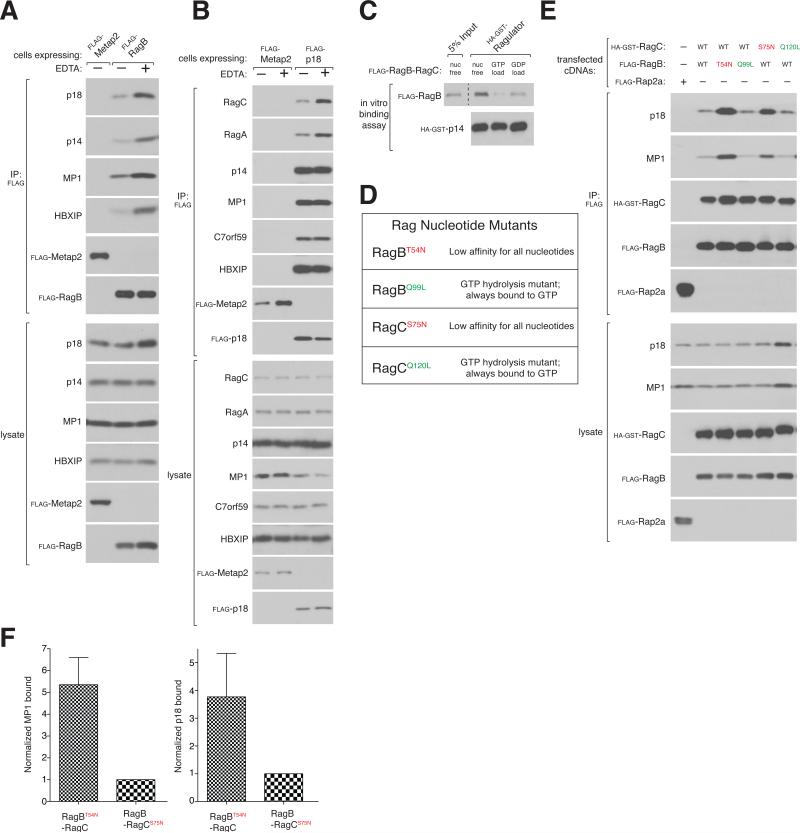
Figure 4. Ragulator preferentially interacts with nucleotide-free RagB.
A) EDTA increases the interaction between endogenous Ragulator and FLAG-RagB. HEK-293T cells stably expressing Flag-RagB were lysed in the absence or presence of EDTA and cell lysates and anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates analyzed by immunoblotting for the levels of the indicated proteins.
B) FLAG-p18 co-immunoprecipitates more endogenous Rags in the presence of EDTA. HEK-293T cells stably expressing FLAG-p18 were treated and analyzed as in (A).
C) Ragulator preferentially interacts with nucleotide-free Rags. In vitro binding assay in which immobilized HA-GST-Ragulator was incubated with nucleotide-free FLAG-RagB-RagC or Rag heterodimers loaded with GTP or GDP. HA-GST precipitates were analyzed for the levels of the indicated proteins.
D) Table summarizing Rag mutants used in this study.
E) The RagBT54N mutant preferentially interacts with endogenous Ragulator. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates were prepared from HEK-293T cells transfected with the indicated cDNAs in expression vectors and analyzed as in (A).
F) Quantification of endogenous MP1 and p18 binding to RagBT54N-RagC and RagBRagCS75N. Each value represents the normalized mean ±SD for n=3. See also Figure S4.