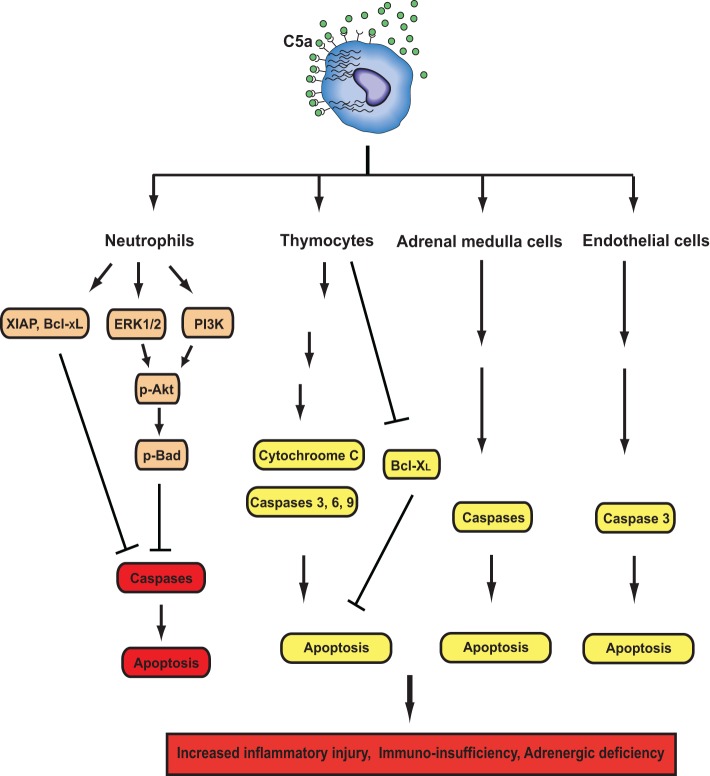
Figure 2.
Effects of C5a signals on apoptosis during sepsis. C5a have both anti- and pro-apoptotic activities depending on cell types. In neutrophils, C5a activates PI3K and ERK1/2 pathways, leading to phosphorylation of Akt and subsequent phosphorylation of Bad. Phosphorylated Bad inhibits cytochrome C release from mitochondria to prevent the formation of the apoptosome, thereby inhibiting neutrophil apoptosis. C5a together with LPS induces XIAP production, which can inhibit the formation of the apoptosome. Sepsis enhances Bcl-xL expression and reduces Bim expression. C5a and LPS can also enhance Bcl-xL expression. All of these events are in favor of maintaining the integrity of mitochondria and preventing neutrophil apoptosis. In thymocyes, adrenal medulla cells, and endothelial cells, C5a can induce apoptosis by enhancing caspase activities or inhibiting Bcl-xL expression.