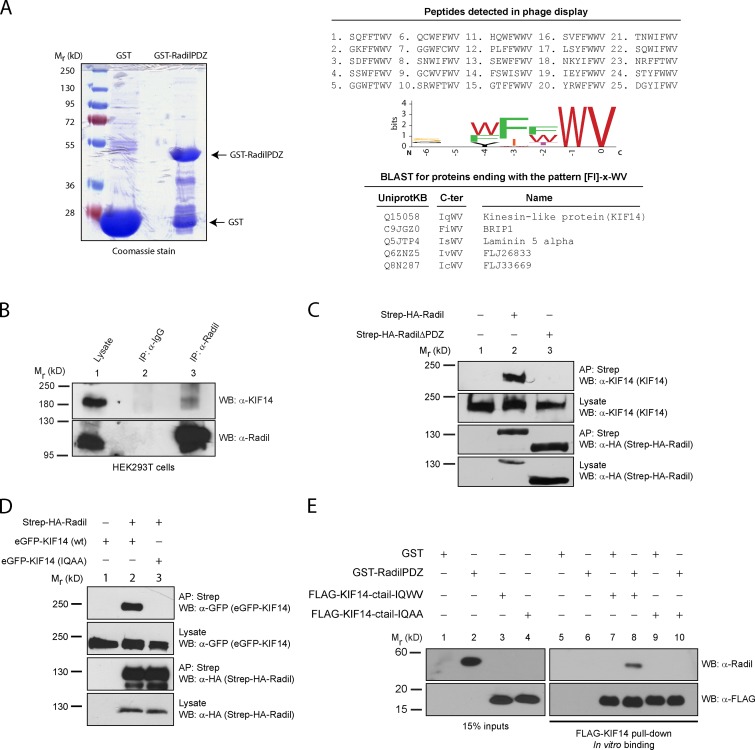
Figure 1.
KIF14 interacts with the Radil PDZ domain. (A) Recombinant GST-RadilPDZ domain was used as bait in phage display selections using a library of random heptapeptides. 25 unique binding peptides were recovered from the screen and analyzed using a sequence logo generator to identify the preferred binding sequence. The resulting C-terminal binding motif [FI]-x-WV was searched against UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot human database; and the C termini of five proteins were found to match this sequence. (B) KIF14 coimmunoprecipitates with Radil. Lysates from HEK293T cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) using α-Radil or control IgG antibodies, followed by Western blotting (WB) with α-Radil or α-KIF14 antibodies. (C) Radil interacts with KIF14 via its PDZ domain. Lysates from HEK293T cells stably expressing Strep-HA-Radil or Strep-HA-RadilΔPDZ were affinity purified (AP) using streptavidin Sepharose followed by WB using α-HA or α-KIF14 antibodies. (D) The KIF14 PDZ ligand is required to bind to Radil. HEK293T cells stably expressing Strep-HA-Radil were transiently transfected with eGFP-KIF14 wild-type (wt) or eGFP-KIF14-IQAA (WV→AA mutant) constructs. Lysates were subjected to AP with streptavidin beads followed by Western blotting with α-KIF14 and α-HA antibodies. (E) Radil binds to KIF14 directly. Recombinant GST-RadilPDZ was incubated with purified FLAG-tagged KIF14-ctail (wild-type or IQAA mutant) that were immobilized on FLAG-M2 beads. After 1 h of binding, beads were washed and protein binding determined by Western blotting using α-Radil and α-FLAG (rabbit) antibodies.