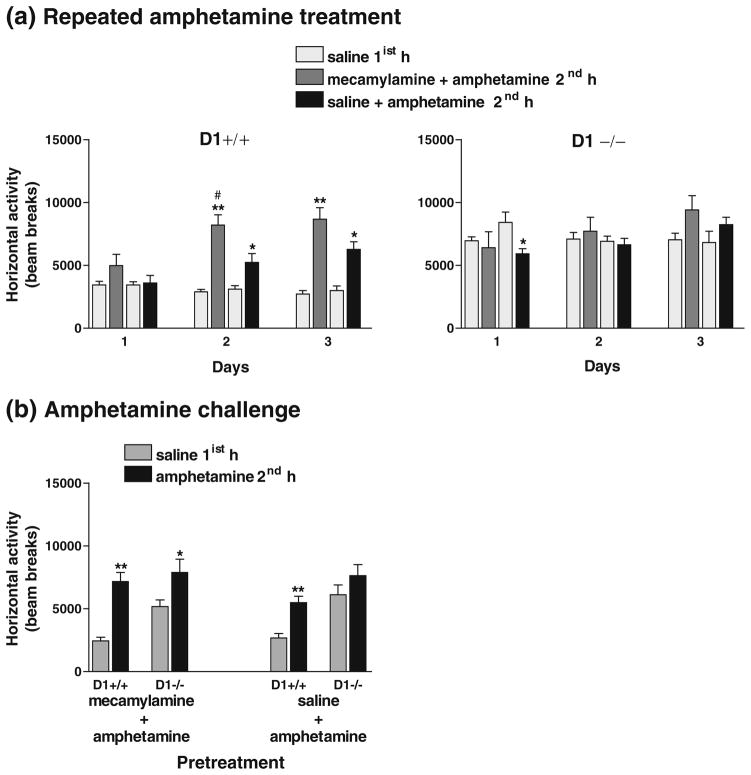
Fig. 10.
Effect of co-administration of mecamylamine and amphetamine or saline and amphetamine on locomotor activity in mice (n=6 per group) during 1-h sessions. a Repeated amphetamine treatments for three consecutive days caused greater augmentation of locomotor activity in D1+/+ mice (P<0.0001) when co-administered with mecamylamine than with saline (P<0.02–0.01), whereas D1−/− mice failed to show any response to either treatment during days 1–2 and exhibited a marginal increase in locomotor activity (P=0.08) on day 3 when amphetamine was co-administered with mecamylamine than with saline. b Amphetamine challenge after 3 weeks of abstinence induced locomotor sensitization in both D1+/+ and D1−/− mice pretreated with mecamylamine + amphetamine and only in D1+/+ mice (but not D1−/− mice) pretreated with saline + amphetamine. *P<0.05–0.001; **P<0.0001 compared to their responses to saline 1 h earlier. #P<0.02 compared to saline + amphetamine treatment. Values are means + SEM