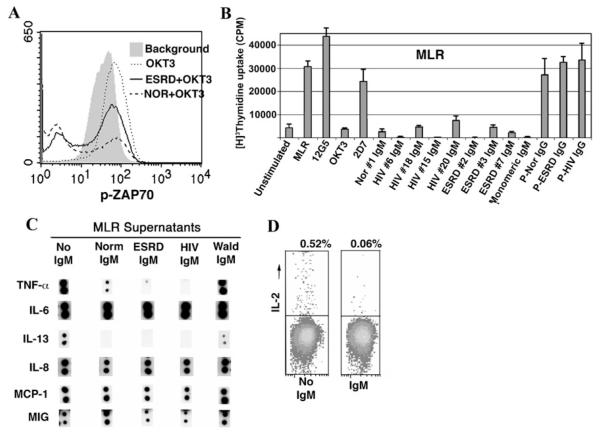
Fig. 3.
Effect of purified IgM on T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. a Data depict flow cytometry histograms of intracellular phos-Zap-70 present in PBL. Note that background phos-Zap 70 (shaded gray) increases after incubating cells with immobilized anti-CD3 for 16 h (MCF increased from 29 to 54). b Effect of pooled normal, ESRD, and HIV IgM on T-cell proliferation induced by alloantigens, i.e., MLR. 15ųg of IgM (including monomeric IgM) were used for 1 × 106 cells/mL in these experiments and added at the time cells were co-cultured. This is a representative example of three separate experiments. The panel depicts MLR proliferation in the presence of individual (labeled #1, #6, etc.) or pooled (P) IgM (4.5 μg/ 0.3 ml), pooled IgG (2 μg/0.3 ml), and murine monoclonal antibodies (2 μg/0.3 mL) to CD3 (OKT3), CXCR4 (12G5), and CCR5 (2D7) when used at the initiation of the MLR. Values for T-cell proliferation assays are mean±SD of experiments performed in triplicate. Panel c. Pooled normal, ESRD, and HIV IgM but not Waldenstrom IgM significantly inhibited the increase in TNF-α and IL-13 but not that of IL-6, IL-8, MIG, and MCP-1 produced in response to alloantigen (MLR) activation of T cells. Panel d Dot plots depicting the effect of IgM on intracytoplasmic IL-2 in PBL activated for 48 h in an MLR. 15ųg of IgM were used for 1 × 106 cell/mL in these experiments. Lobo PI, Schlegel KH, Spencer CE, Okusa MD, Chisholm C, Mchedlishvili N, et al.: Naturally occurring IgM anti-leukocyte autoantibodies (IgM-ALA) inhibit T cell activation and chemotaxis. J. Immunol, 180:1780-1791, 2008. Copyright 2008. The American Association of Immunologists, Inc