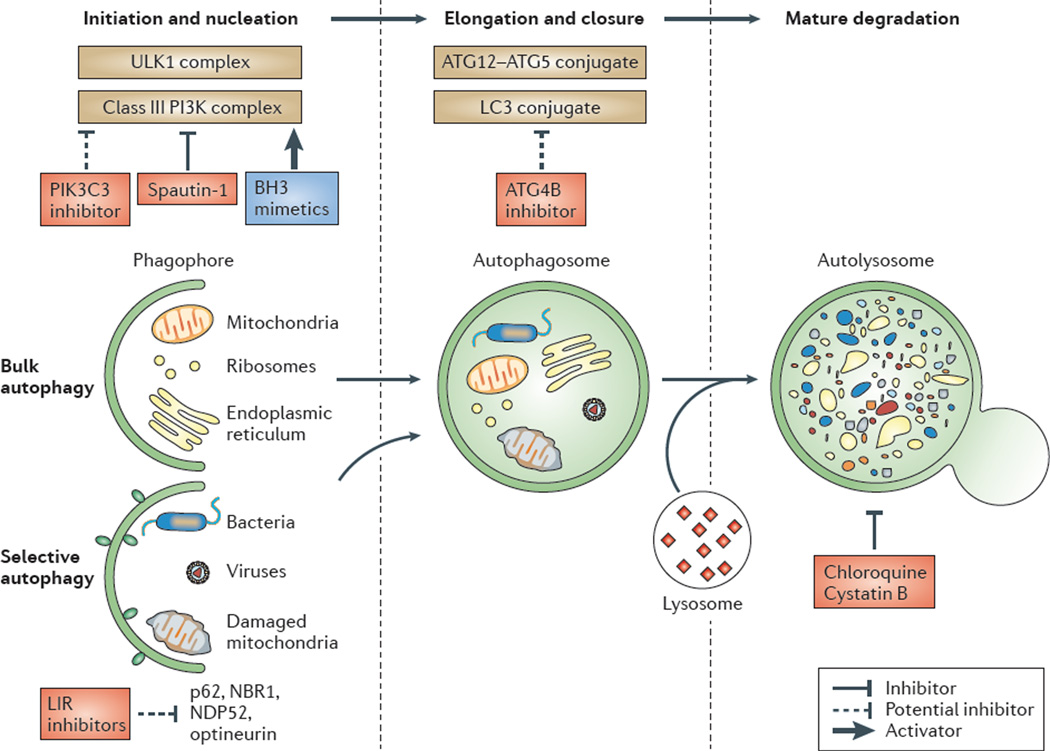
Figure 2. Effects of drugs on the different steps of the autophagic pathway.
The formation of the autophagosome depends on the initiation and/or nucleation of a specific membrane structure known as the phagophore, and on the elongation and closure of the phagophore to form a double-membrane-bound vacuole. The biogenesis of autophagosomes requires the ordered intervention of autophagy-regulated (ATG) proteins that act on different modules. Some of these modules are shown on the figure, including the UNC51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) complexes, ATG12 (the ATG12–ATG5 complex) and microtubule-associated protein 1 light-chain 3 (LC3; for example, the LC3–phosphatidylethanolamine conjugates); ATG4B is a protein that is involved in the regulation of LC3 lipidation and delipidation. The ULK1 complex is composed of ULK1 (the mammalian orthologue of yeast Atg1) and RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1 (RB1CC1; also known as FIP200; the mammalian orthologue of yeast Atg13, Atg17 and Atg101). The PI3K complex is composed of beclin 1 (the mammalian orthologue of yeast Atg6 and Atg14), class III PI3K (PIK3C3), PIK3R4 (PI3K regulatory subunit 4) and AMBRA1 (activating molecule in BECN1-regulated autophagy protein 1). Both complexes congregate at the phagophore assembly site to initiate autophagy in response to nutrient starvation. The kinase activity of ULK1 is controlled by the kinase mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1), which is sensitive to rapamycin220. The protein ATG14 appears to have a key role in the targeting of the PI3K complex to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). How the ULK1 and PI3K complexes are coordinately regulated remains to be elucidated. The production of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) by human PIK3C3 recruits the PtdIns3P-binding proteins ATG18 (also known as WIPI1 and WIPI2) and double FYVE domain-containing protein 1 (DFPC1). Cargos can be incorporated into autophagosomes in a non-selective manner (known as bulk autophagy) or in a selective manner (known as selective autophagy). Maturation occurs when the autophagosome fuses with the endolysosomal compartment. The final degradation of cargos occurs in autolysosomes. The activity of the class III PI3K complex can be manipulated by both activators (such as BH3 (BCL-2 homology 3) mimetics) and inhibitors (such as spautin-1; specific and potent autophagy inhibitor 1). PIK3C3, which is a component of the class III PI3K complex, is a potential target for drugs. Some other potential targets are also indicated on the figure. Autophagosome closure can be inhibited by reducing ATG4B activity. Compounds that interfere with LC3-interacting region (LIR) motifs could potentially block the selective recruitment of cargos such as mitochondria, viruses and bacteria. Inhibitors of lysosomal enzymes (such as cystatin B), and lysosomotropic agents that increase the lysosomal pH (such as chloroquine and hydrochloroquine) block the degradative activity of autolysosomes. NDP52, nuclear dot protein 52; p62, ubiquitin-binding protein p62 (also known as sequestosome 1).