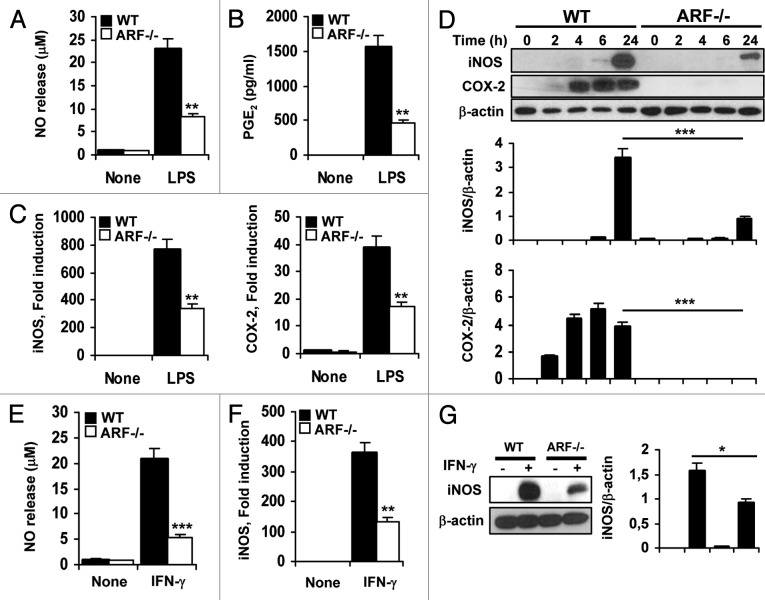
Figure 2. Attenuated inflammatory response of ARF deficient macrophages to classical activation. (A) Peritoneal WT and ARF-deficient macrophages were stimulated with 200 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 h and NO release was determined by the Griess reaction. (B) PGE2 levels were assessed by ELISA in cells treated as in A. (C) Peritoneal macrophages from WT and ARF-deficient mice were activated for 6 h with 200 ng/mL LPS and expression of iNOS and COX-2 was evaluated by quantitative PCR. (D) Protein levels of iNOS and COX-2 were evaluated by immunoblotting after stimulation of peritoneal macrophages with 200 ng/mL LPS for the indicated time. Band intensities were quantified by densitometry, normalized to β-actin levels and represented as means ± SD of the fold change from control condition (n = 3). (E) NO release of peritoneal macrophages from WT and Arf−/− mice after stimulation for 24 h with 50 ng/mL γinterferon γ (IFNγ). (F) iNOS induction was examined by quantitative PCR in WT and Arf−/− cells after treatment with 50 ng/mL IFNγ for 6 h. (G) Protein levels of iNOS were evaluated by immunoblotting after stimulation of peritoneal macrophages with 50 ng/mL IFNγ for 24 h. Results were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and data are reported as means ± SD *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 as compared with the same condition in WT macrophages. (D) and (G) are representative of one out of three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.